Mazda aspires to be a company that coexists in harmony with the planet and is committed to exhaustive resource recycling and waste reduction measures. Development-related resource recycling measures include the promotion of the 3Rs (reduce, reuse, and recycle) and circular economies for a perspective encompassing the entirety of automobile life cycles. Meanwhile, the Company will advance initiatives in production, logistics, and other areas to contribute to the realization of a recycling-oriented society from a “well-to-wheel” perspective and global and supply chain perspective with a view of the entirety of the automobile supply chain.
PROMOTING RESOURCE CIRCULATION
Materials
Basic Approach (Materials)
Goals (Materials)
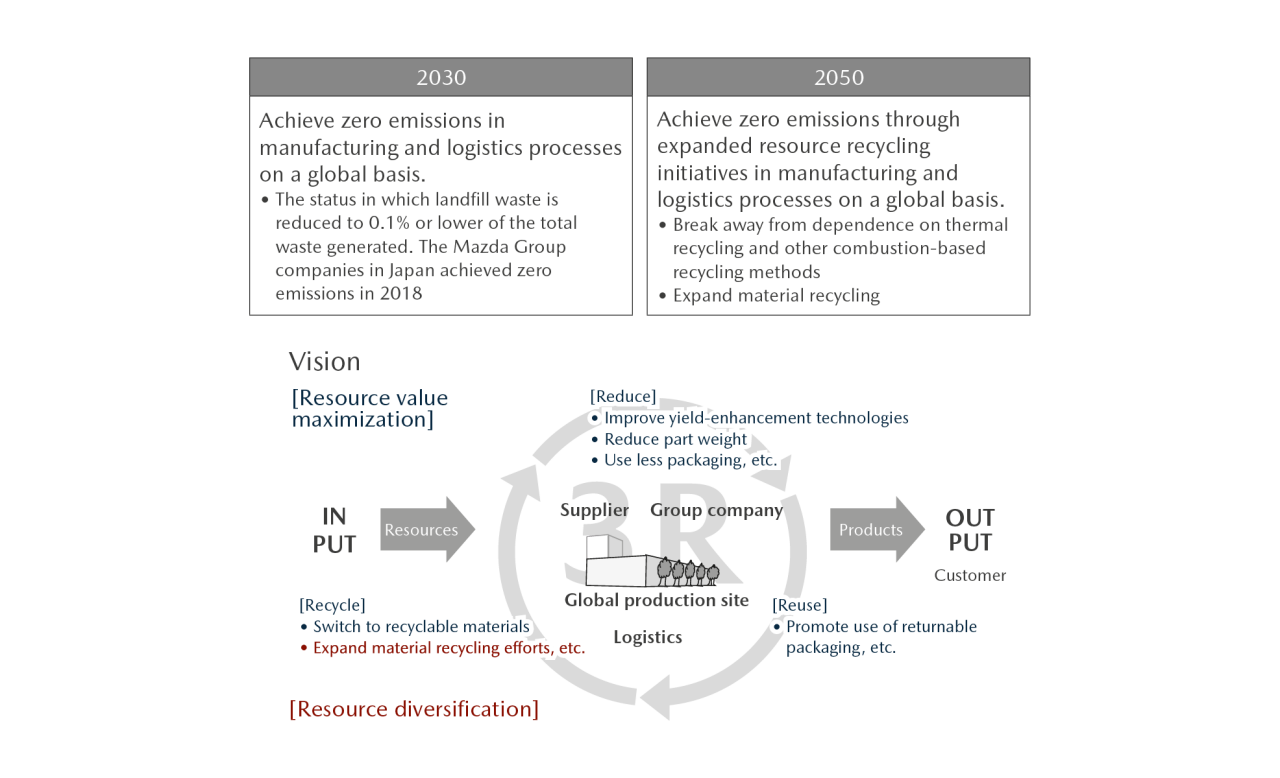
The Mazda Group continues to expand its global efforts to achieve zero emissions and recycle resources through such means as efficiently using resources to prevent waste and promoting the 3Rs + Renewable.

Initiatives (Materials)
Product and Technology Development
Product Development and Design with Consideration for Recycling Needs
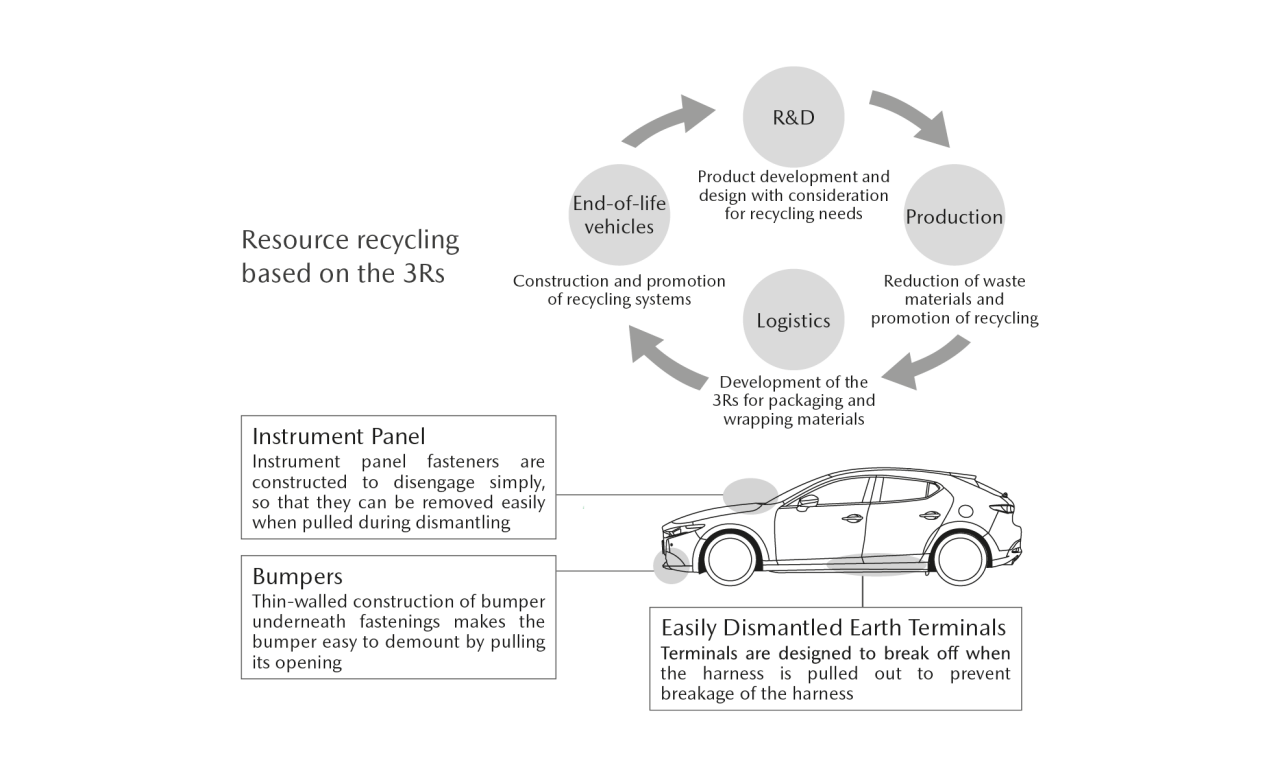
Many limited resources, such as steel, aluminum, plastics, and rare metals, are used to manufacture vehicles. Mazda is incorporating 3Rs design into all vehicles currently under development to increase the recyclability of its new vehicles.
【Specific Initiatives】
- Research into vehicle design and dismantling technologies that simplify dismantling and separation to make recyclable parts and materials easier to remove
- Use of easily recyclable plastics, which constitute the majority of automobile shredder residue (ASR)※ by weight
※ ASR refers to the residue remaining after the crushing or shredding of what is left of the vehicle body (following the removal of batteries, tires, fluids, and other parts requiring appropriate processing as well as the removal of engines, bumpers, and other valuable parts) and separating and recovering metals.
Resource Recycling based on the 3Rs

Expanded Adoption of Biomaterials
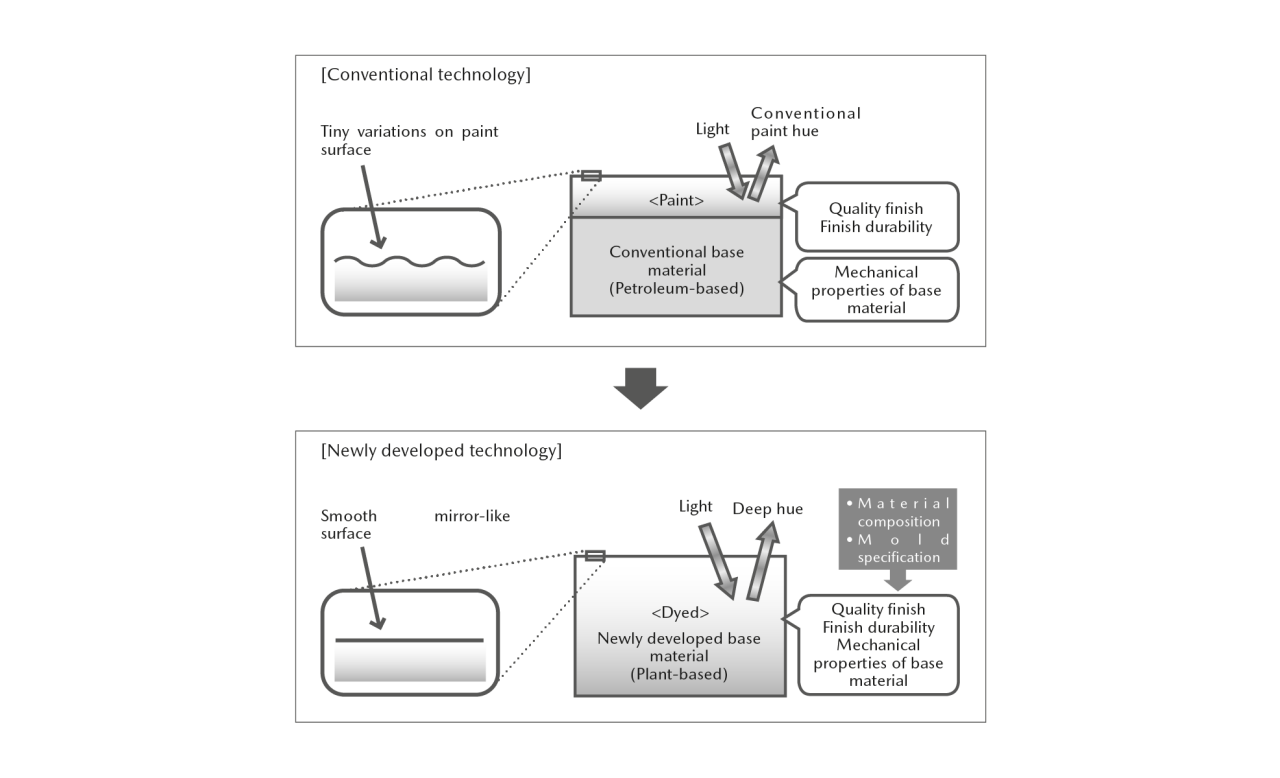
Mazda has been proactively developing plant-derived biomaterials which have the potential to help reduce environmental impacts by curbing the use of fossil fuels and CO₂ emissions. In 2006, the Company became the first in the automotive sector to develop high heat-resistant, high-strength bioplastic for vehicle interior parts. In 2007, Mazda succeeded in the development of the world’s first*1 biofabric for vehicle seat covers made with completely plant-derived fibers. In 2014, bio-based engineering plastic*2 suitable for use in vehicle exterior parts was developed by the Company. Mazda is currently expanding its adoption of this material.
*1 As of September 2007; according to Mazda data
*2 Bio-based engineering plastic was developed by Mazda Motor Corporation in collaboration with Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation.
Technology Development Initiatives Related to Bio-Based Engineering Plastics
■2014: Mazda developed bio-based engineering plastic featuring a high-quality finish without painting. By developing paint-less technology for interior and exterior parts taking advantage of the characteristics of this material, the Company not only secured the excellent environmental performance of the material but also achieved a high-quality finish that could not be achieved with conventional paint, thereby contributing to environmental protection while reducing production cost by eliminating the painting process.
■2017: Mazda developed materials suitable for making large, intricately shaped exterior parts, such as front grilles, and optimized the die specifications in order to substantially enhance the formability of these parts. In 2020, the Company received the Award for Science and Technology (Development Category) of the 2020 Commendation for Science and Technology by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology for the development of the aforementioned bio-based engineering plastic.
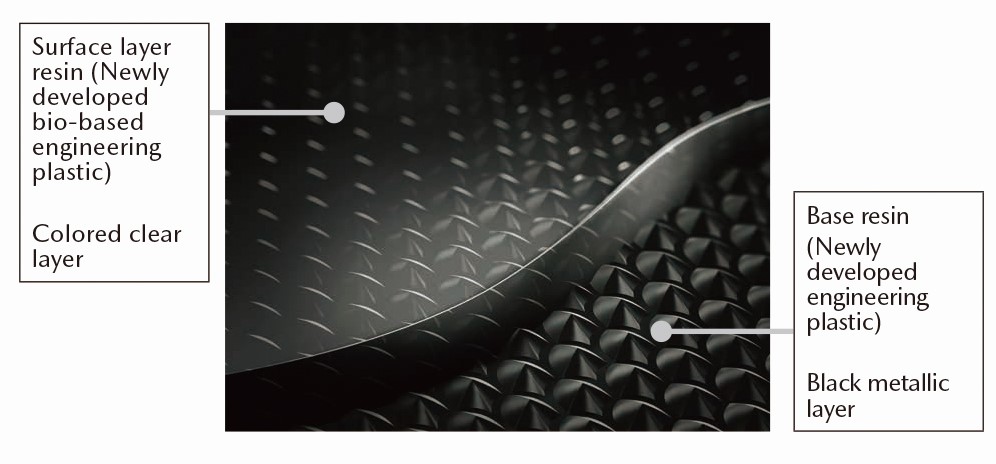
■2018: Mazda developed a new technology for two-layer molding of pattern designed bio-based engineering plastic, which enables the molding of a transparent surface layer and a base layer with a pattern-engraved surface, both of which are made of eco-friendly bio-based engineering plastic. The new technology reduces environmental impacts while making it possible to provide elaborate shaded patterns of deep color, which was not possible with the prior technology. In 2021, the Company received the Aoki Katashi Innovation Award from the Japan Society of Polymer Processing for the development of the aforementioned new technology for two-layer molding of pattern designed bio-based engineering plastic.
■2023: Mazda received a METI Minister’s Prize at the Ninth Monodzukuri Nippon Grand Awards.
Paint-Less Technology for Interior and Exterior Parts Taking Advantage of Bio-Based Engineering Plastic (Developed in 2014)

New Technology for Two-Layer Molding of Pattern Designed Bio-Based Engineering Plastic (Developed in 2018) Surface View of New Technology for Two-Layer Molding of Pattern Designed Bio-Based Engineering Plastic


Production and Logistics
Production Materials:Maintenance of Zero Landfill Waste Status and Reduction of Waste
To reduce landfill waste at its four principal domestic sites※ to zero, Mazda is promoting reductions in the volume of manufacturing by-products and waste, more rigorous sorting of waste, and recycling. The Company was thereby able to achieve zero landfill waste, and it has maintained this status from FY March 2009 to FY March 2024. The Company has also been recycling materials to ensure that packaging materials used in the vehicle and transmission assembly processes can be reused as raw materials through stricter sorting of packaging by material and quality.Furthermore, Mazda has been proactively utilizing recycled materials for the plastic pallets used to transport parts overseas. Currently, the Company is examining the possibility of reusing plastic waste generated at its plants as a recycled material for the production of plastic pallets, which is anticipated to further reduce the amount of waste generated.
【Statistics from FY March 2024】
Reduction in total amount of waste generated of 84% in comparison to FY March 1991
Environmental data (Amount of landfill waste, amount of recycled materials, recycling ratio)
※ Headquarters (Hiroshima); Miyoshi Plant; Hofu Plant, Nishinoura District; and Hofu Plant, Nakanoseki District (including non-manufacturing areas such as product development)
Logistic Materials: Reduction of Volume of Packaging and Wrapping Materials
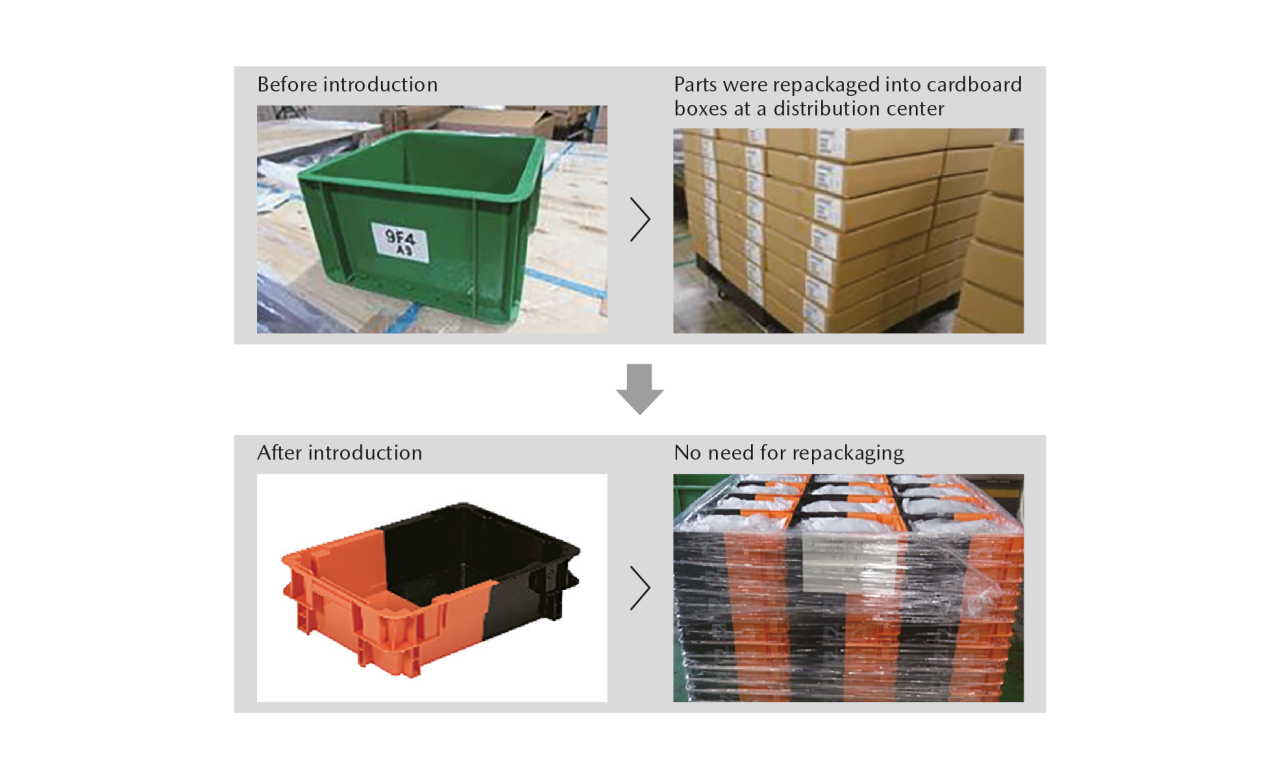
Mazda is moving forward with 3Rs initiatives including using returnable containers, simplifying packaging specifications, and recycling materials. In regard to the transportation of repair parts in Japan and overseas and the export of parts to overseas factories, coordination was promoted between departments in five areas—development, production, procurement (purchasing), logistics, and quality—in FY March 2017 to optimize parts procurement and vehicle manufacturing from the stage of product development and to establish strong cooperation with the supply chain. These efforts resulted in reduced volumes of packaging and wrapping materials and an increased packaging filling rate. In FY March 2024, we continued to promote coordination between these departments to improve the packaging filling rate for some parts and to reduce the volumes of packaging and wrapping materials. Mazda will continue promoting and expanding activities through coordinated efforts between different departments so as to reduce the consumption of materials.
【Statistics from FY March 2024】
Reduction in volumes of packaging and wrapping materials used of 18.9% in comparison to FY March 2020
As for repair parts for overseas, the Company continues to expand the application of large-size returnable containers with the aim of increasing the container filling rate. For the parts exported to overseas assembly plants, the Company is now expanding its introduction of new standard containers for parts to be transported in containers from Japan. This makes it possible to eliminate the empty space inside of containers. By improving the filling rate inside of containers from 70% to 90%, the Company looks to reduce the number of containers and the number of transportation truck services used, thereby contributing not only to the reduction of the use of packaging and wrapping materials but also to the reduction of CO₂ emissions. As of March 31, 2024, we had nearly completed introduction of the new standard containers at factories in the United States, China, Mexico, and Thailand. The Company is planning to expand the introduction of the new standard containers to achieve further reductions.
【Statistics from FY March 2024】
Reduction of approximately 224 tons in use of packaging and wrapping materials through shift to returnable containers
Environmental data (Consumption of wrapping and packaging materials)
Overview of Coordinated Initiatives
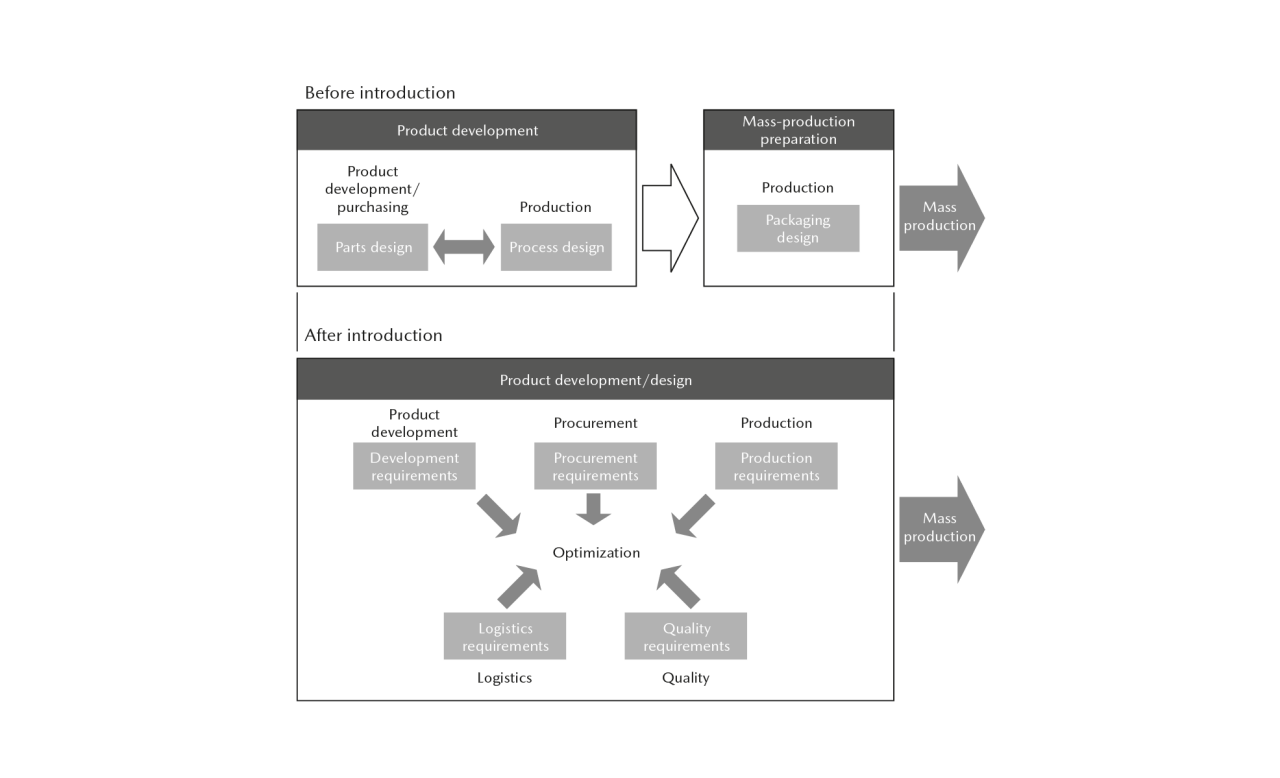

Introduction of Returnable Containers


Collection and Recycling of Vehicles and Parts
Almost all materials used in vehicles can be recycled. Implementing thorough recycling and waste reduction initiatives to ensure that limited resources are used effectively, Mazda promotes efforts to contribute to the realization of a recycling-oriented society.
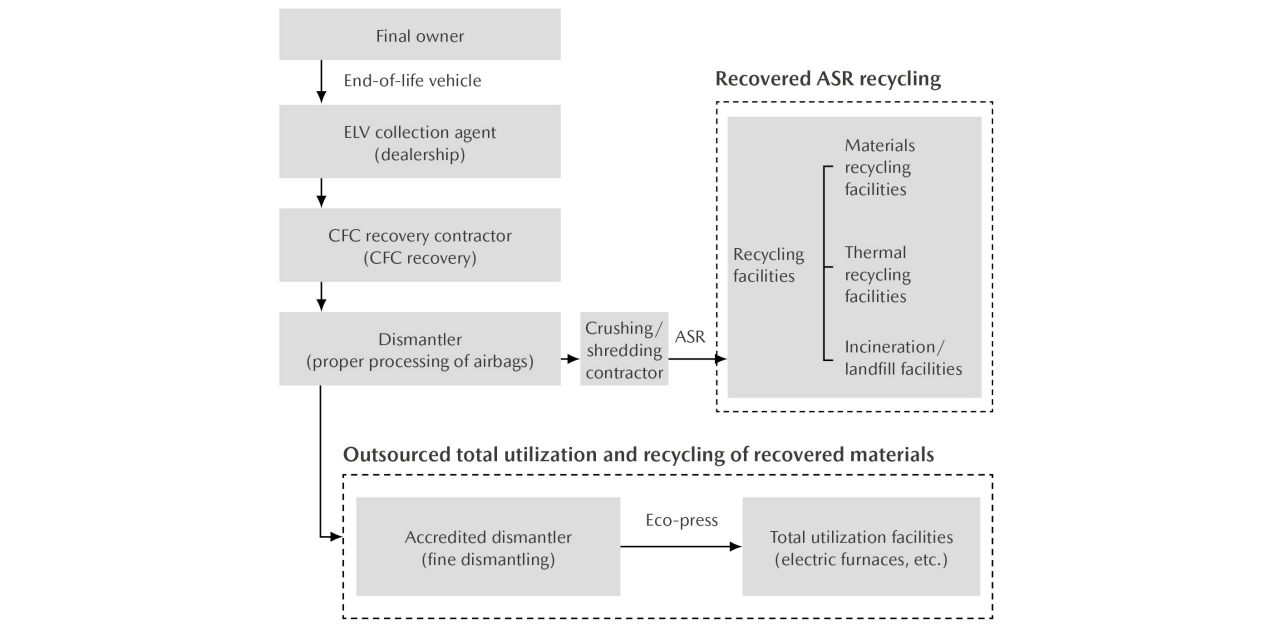
Measures in Response to Japan’s Act on Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles
Mazda properly processes three designated items in accordance with the Act on Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles (chlorofluorocarbons, airbags, and ASR). In addition, the Company is actively working to recycle these items through unique technologies and measures. In regard to ASR, Mazda is working through the Automobile shredder residue Recycling promotion Team (ART), a consortium of 12 companies including Mazda, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., and Mitsubishi Motors Corporation, to comply with the law and achieve progress in the reuse of resources. The Company also promotes recycling at dealerships. Dealerships collect vehicle recycling fees at the time of sale of new vehicles and collect end-of-life automobiles from their final owners in order to transfer them to disposal processing companies. As for recycling fees, the Company reviewed its fee calculation standard for new models launched in 2012. The new fee standard is applicable to the Company’s new models released after that. Based on predictions of future recycling trends, the Company will continue to push forward with its recycling business in such a way to ensure a balance between revenue and expenditures over the medium to long term.
The Act on Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles was revised in February 2012 to include lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries as items for advance collection before dismantling of end-of-life automobiles. Mazda is committed to collecting LiBs installed in vehicles launched in and after October 2012 through the LiB Joint Collection System of Japan Auto Recycling Partnership, Ltd. The Company also independently collects NiMH batteries installed in the Axela (Mazda3 overseas) Hybrid (launched in November 2013). Moreover, Mazda publishes the disposal work procedure guidelines on its website and promotes appropriate disposal to ensure that the relevant business operators can safely recycle vehicles using LiBs and NiMH batteries as well as those equipped with deceleration energy regeneration system capacitors.
End-of-Life Automobile Recycling Process

Resource Recycling Results in FY March 2024
| Number of vehicles from which ASR is collected |
114,054units | |
| Number of vehicles from which airbags are collected | 110,363units | |
| Number of vehicles from which chlorofluorocarbons are collected |
108,118units | |
Recycling ratios |
ASR | 96.7% |
| Airbags | 97.1% | |
| Recycling ratio for end-of-life automobiles* |
More than 99% | |
| Total contracting deposits received |
1,399,396,891yen | |
| Total expenses for recycling |
1,363,281,529yen |
* Recycling ratio for end-of-life automobiles is the recycling ratio in dismantling and shredding processes of around 83% (cited from the May 2003 joint council data), plus the remaining ASR ratio of 17% multiplied by the ASR recycling rate for the relevant fiscal year.
ASR and Japan’s Act on Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles
Disposed vehicles consist of about 80% useful metals and about 20% automotive ASR that includes resin. Useful metals are recycled in cooperation with metal recycling-related companies such as dismantlers, crushing and shredding contractors, and steel manufacturers. ASR, which used to be disposed by landfill, is now subject to the Act on Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles, which was enacted in January 2005. This law was instituted in response to the rise in the risk of illegal dumping of end-of-life automobiles on the back of a surge in disposal costs due to overstrained final landfill sites and low iron scrap prices. Following the enactment of this law, car manufacturers are responsible for recycling chlorofluorocarbons, which lead to global warming and ozone depletion; airbags, which require specialist knowledge for disposal; and ASR using recycling fees deposited by final owners of end-of-life automobiles.
Recycling of End-of-Life Automobiles Overseas
Mazda is committed to the recycling of end-of-life automobiles overseas in accordance with the laws in each country and region through efforts centered on local distributors. In countries planning to implement recycling-related laws, Mazda is preparing to respond in cooperation with the distributors in these countries. For vehicles equipped with LiBs and capacitors, the Company publishes disposal work procedure guidelines on its website and promotes appropriate disposal, as is also done in Japan, to ensure that the relevant business operators are able to safely dispose of these vehicles.
Europe
Based on EU directives, Mazda Motor Europe GmbH provides dismantling manuals to recycling contractors when introducing new models and has established a network to collect used vehicles from their final owners free of charge in cooperation with local distributors.
China
In accordance with a law enacted in January 2015, local manufacturers are managing substances with environmental impact and developing dismantling manuals.
Collection and Recycling of Used Parts in Japan
Mazda conducts ongoing efforts to collect damaged bumpers replaced through repairs so they can be recycled as plastic materials for use in new vehicle bumpers and other items.
■ Recycling of damaged bumpers: Mazda collects bumpers removed for repairs at dealerships throughout Japan and recycles them for reuse as plastic parts (new vehicle bumpers, undercovers, etc.).
【Statistics from FY March 2024】
・Collection of 43,889 damaged bumpers to be recycled
Water
Basic Approach (Water)
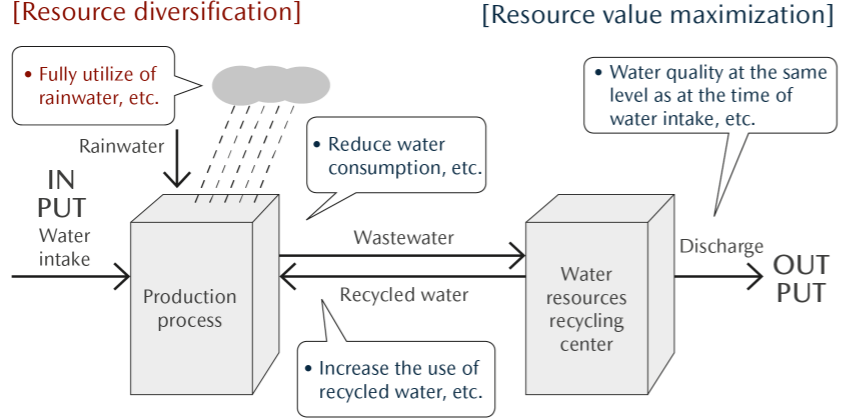
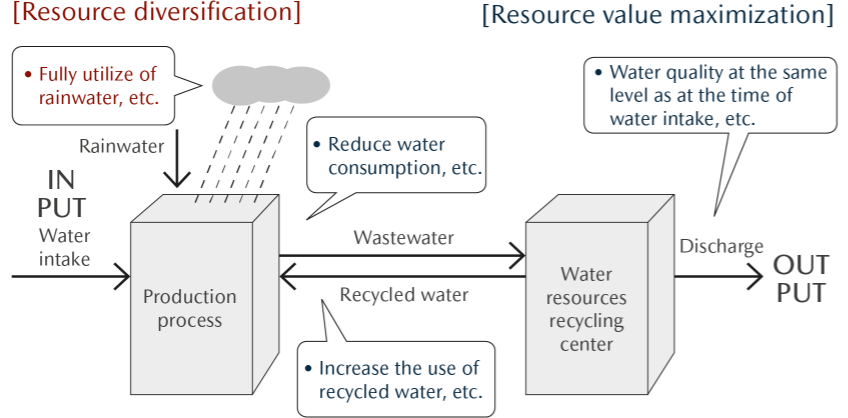
To conserve water resources, the Mazda Group promotes activities to eliminate wasteful water use and circulate water resources by treating used water so that it is the same quality as when it was taken from nature.
| 2030 |
|---|
Implement an optimal approach to water resources recycling and circulation at a model plant* in Japan. • Fully utilize water without any waste, as a valuable resource that is a natural blessing. • Circulate water as a valuable resource that is a natural blessing, by treating used water so that it is the same quality as before it was used, and returning it to nature. |
| 2050 |
|---|
Implement an optimal approach to water resources recycling and circulation in global manufacturing processes. • Fully utilize water without any waste, as a valuable resource that is a natural blessing. • Circulate water as a valuable resource that is a natural blessing, by treating used water so that it is the same quality as before it was used, and returning it to nature. |
*Model plant: A pilot plant where new attempts are made, ahead of other facilities.
Vision
Goals (Water)
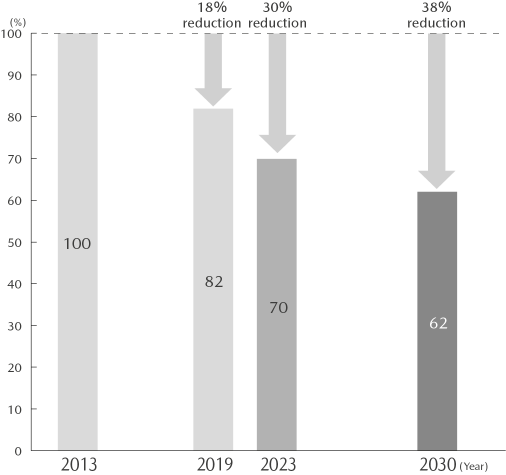
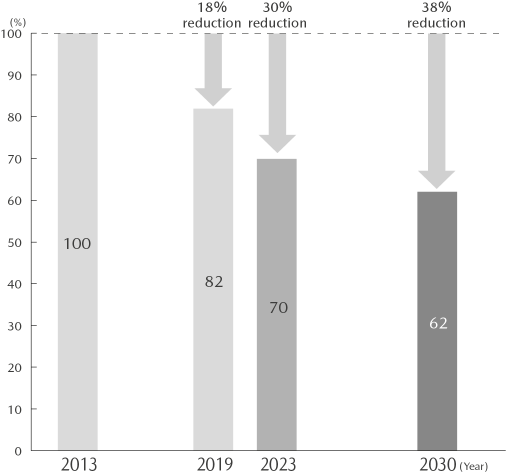
To guide its water resource reuse and recycling initiative at a domestic model plant, the Company has set a target of reducing water intake by the entire Mazda Group in Japan by 38% in 2030 compared with 2013 levels. In order to achieve this target, the Company aims to reduce the annual water use by 2%. In addition, the Company promotes the further use of rainwater and recycled water.
Water intake amount by domestic Mazda Group companies
Initiatives (Water)
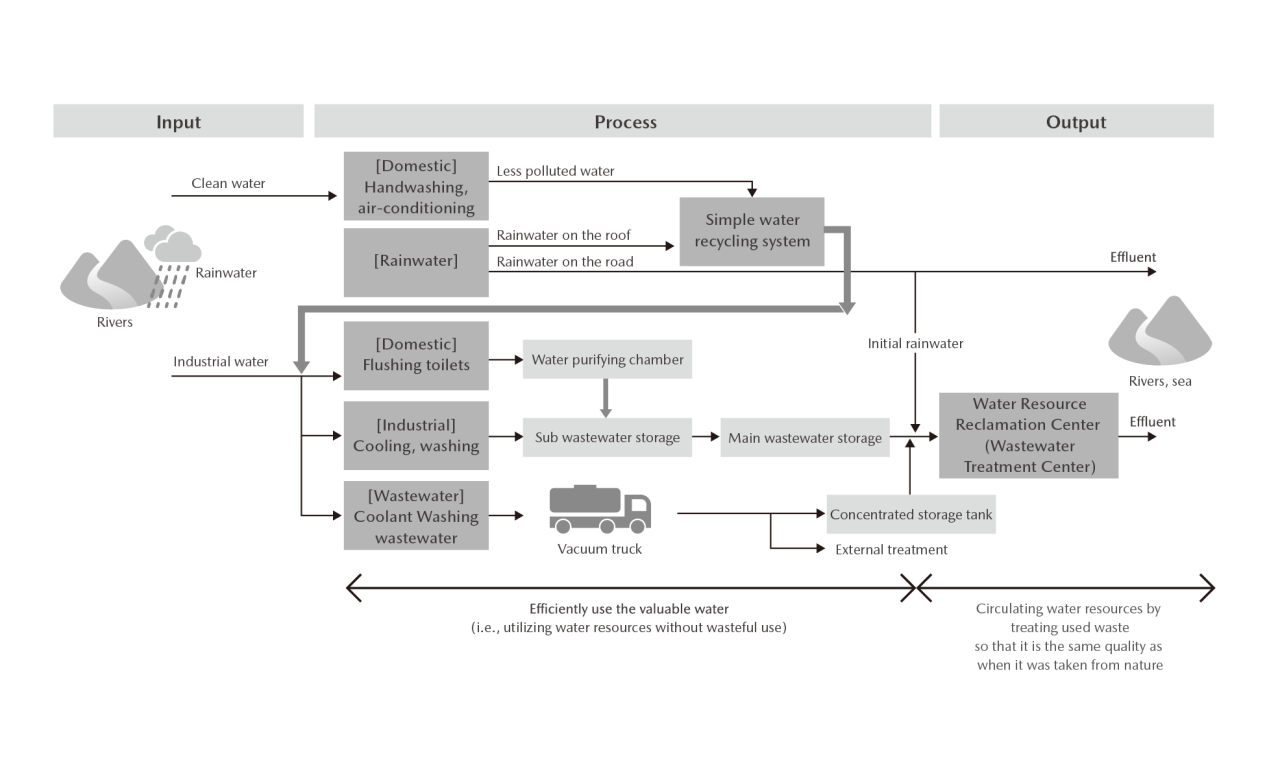
Water Resource Preservation
By clarifying inputs, processes, and outputs involving water resources in its business activities, Mazda is promoting initiatives to efficiently use these valuable resources (i.e., utilizing water resources without wasteful use). We thereby seek to minimize water usage and circulating water resources by treating used water so that it is the same quality as when it was taken from nature. To advance these initiatives, the Water Resource Group※ was established consisting of members in charge of water resource conservation. Six major themes have been defined for the activities of this group: (1) Elimination of wasteful use, (2) Reduction, (3) Reuse, (4) Recycling, (5) Utilization of rainwater, water sludge, and waste fluid, and (6) Building of communities and systems and development of human resources. Moreover, the group is divided into two teams that are tasked with analyzing current conditions and responding to issues identified during said analyses. The Water Resource Group has also started sharing information on initiatives at domestic plants with overseas plants as well as supporting overseas plants’ efforts to address relevant issues.
・ Recycling and Circulation Team:
Studies models in the field of wastewater treatment and reviews models and implements trials in the field of water intake
・ Use Reduction Team:
Introduces models and introduces results of trials reviewed by the Recycling/Circulation Team at plants
※ The Water Resource Group is a working group affiliated with the Business Site Environment Committee, an organization that examines and promotes environmental protection methods in manufacturing and logistics and measures for reducing environmental impacts throughout the entire supply chain.
Examples of Initiatives for Efficient Use of Water Resources
【Appropriate Use and Reuse】
・Appropriate drainage of cooling towers:
Prevention of overflows caused by excessive water supply and reuse of less-polluted water in circulation without draining in accordance with internal standards
・Conservation of toilet flushing water:
Installation of sensor on toilets that allow flushing only when the sensor detects the presence of the user
・Efficient use of water for vehicle body cleaning processes at painting facilities:
Efficient use of water in cleaning processes through management of electrical conduction and utilization of bacteria removal devices so that cleaning process water can be reused
【Recycling of Wastewater and Utilization of Rainwater】
Recycling of less-polluted water, such as hand washing water and air conditioning drainage, through simple recycling systems so that it can be used together with stored rainwater for flushing toilets, watering green spaces, and other applications at Mazda sites