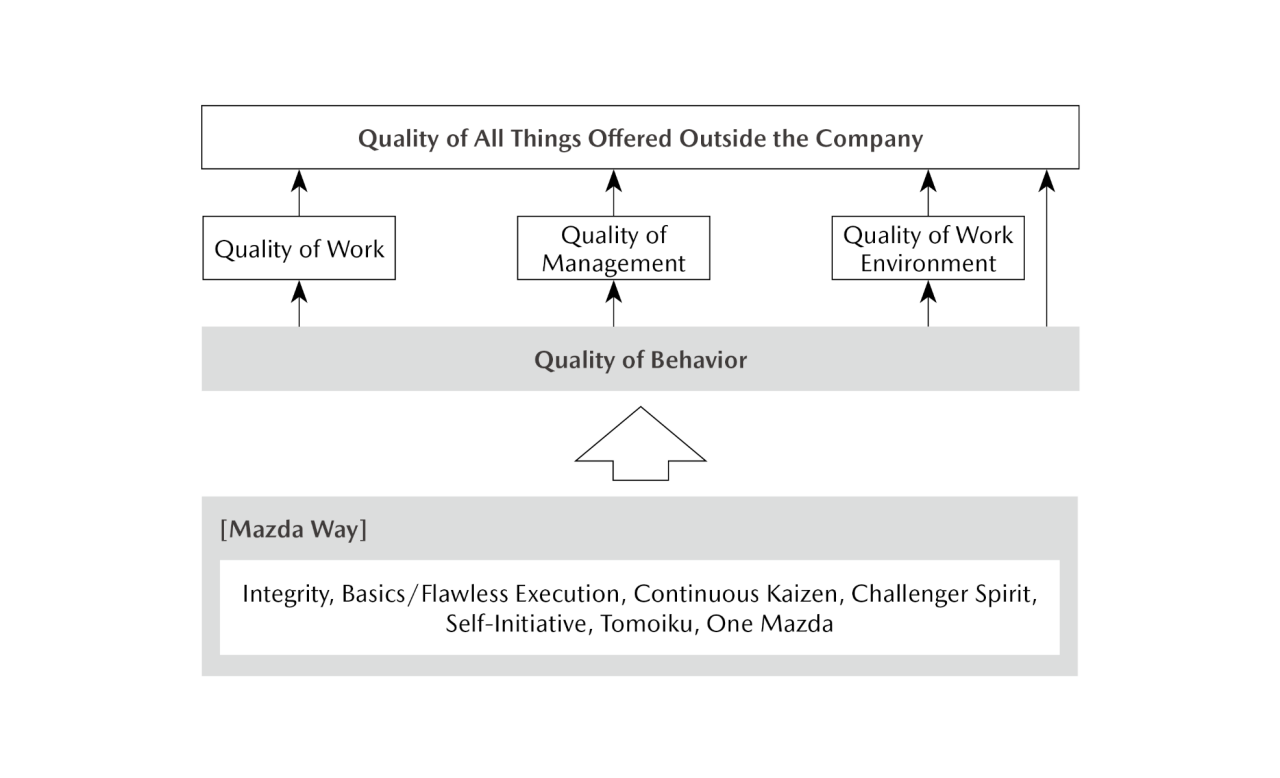
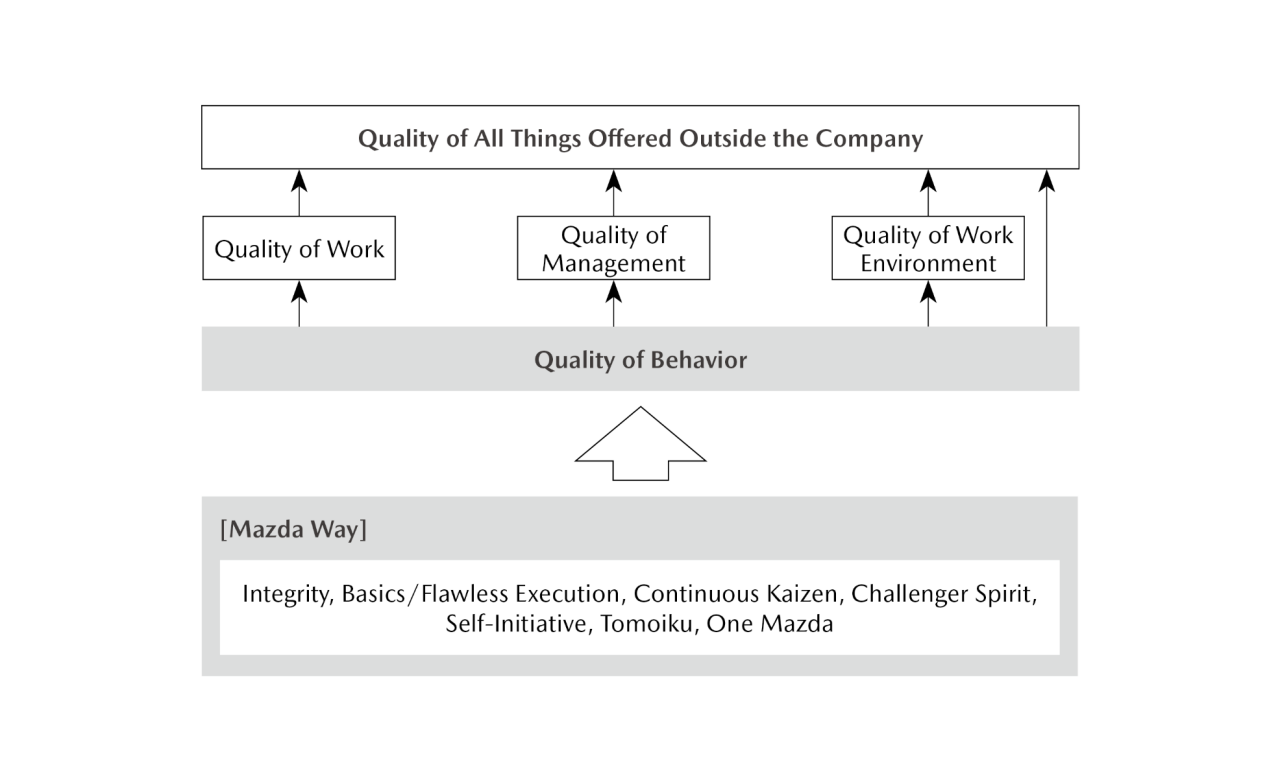
Mazda believes that it is important to enhance the quality of all things offered outside the Company, including products and services, to satisfy customers as it seeks to exercise its corporate philosophy. The Company has defined the Five Types of Mazda Quality: quality of work, quality of management, quality of work environment, quality of behavior, and quality of all things offered outside the Company, which is underpinned by the preceding four. In line with its quality policy, the Company continues to evolve its initiatives and promote united collaboration among all areas of operation to further enhance Mazda’s unique value.
IMPROVING QUALITY
Basic Approach
Mazda Quality Policy
To enrich the lives of our customers by providing products and services that reflect steady and uncompromising work
Five Types of Mazda Quality
Approach toward Quality Improvement
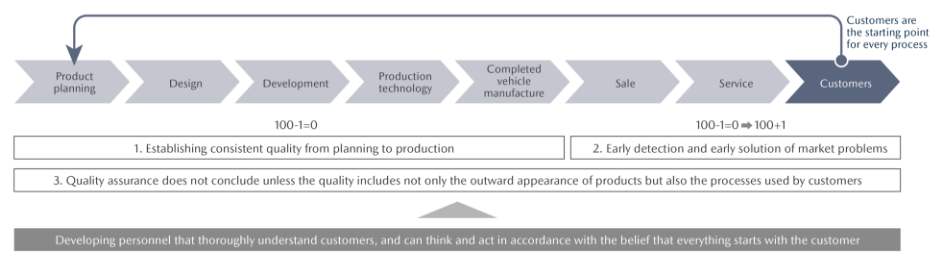
To deliver customers safety, trust, and excitement through automotive lifestyles and to ensure that customers always feel the value of its products, Mazda positions customers as the starting point of all of its business activities and makes Groupwide efforts based on the following Vision for Quality Assurance. The Company recognizes that quality assurance does not conclude unless the quality includes not only the outward appearance of products but also the processes used by customers. Accordingly, the Company works diligently to develop personnel who thoroughly understand its customers, and who can think and act in accordance with the belief that everything starts with the customer.
Vision for Quality Assurance
【Vehicle production based on the “100 – 1 = 0” belief 】
1. Consistent quality from planning to production:
The “100 – 1 = 0” belief expresses Mazda’s strong desire to provide good quality to all customers under the belief that if even only one out of 100 vehicles is found to be defective, the car has no value for the customer. Mazda pursues a kind of vehicle production that respects each vehicle as a certain customer’s one-and-only, and aims to achieve zero defects. In keeping with the basic principles of manufacturing and based on a full understanding of its mechanisms, all related departments work in close collaboration to establish consistent quality in all processes, ranging from planning to production.
【Initiatives for the process of changing “100 – 1 = 0” to “100 + 1” 】
2. Early detection and early solution of market problems:
If an unpredictable problem arises in the market, it may result in loss of trust from customers (“100 – 1 = 0”). To avoid this situation, Mazda promotes quality assurance activities for the early detection and early solution of any trouble pointed out by customers.
3. Creation of an emotional connection with customers:
Through consistently earnest engagement with customers as well as close communication, Mazda aims to forge special bonds with customers based on enduring trust (“100 – 1 = 0” → “100 + 1”).
Mazda Quality Management System
To make faithful and unceasing efforts and constantly ensure quality in products, sales, and after-sales services that can always satisfy the expectations and live up to the trust of customers, Mazda has established the Mazda Quality Management System based on ISO 9001,* and has applied it to the series of processes spanning from product development to production, sales, and after-sales services. At overseas production sites, the Company promotes the establishment of systems that encourage local employees to take autonomous action to improve quality and is advancing the acquisition of ISO 9001. The Company thereby aims to drive improvements in the quality of Mazda vehicles, which are produced and sold worldwide. Global quality managers are responsible for practicing regular communication with representatives from each region who are most closely connected to local markets in order to gather input from the front lines on whether the Company is living up to the expectations and trust of customers. This communication helps facilitate the quick resolution of issues. Furthermore, quality representatives for each region participate in meetings where they share best practices with the goal of enhancing Mazda’s global quality.
* ISO 9001 is a set of international standards for quality management and assurance.
Acquisition of ISO 9000 Series
Year of Acquisition
|
Types of ISO Certification | Certified Organization, Product, Service, Etc. |
|---|---|---|
| 1994 | ISO 9002 | Mazda Motor Corporation: Vehicles produced at Hiroshima Plant and Hofu Plant(The first Japanese automobile manufacturer to be certified) |
| 1996 | ISO 9001 | Mazda Motor Corporation: Engineering, product development, manufacturing, and after-sales service |
2001 |
ISO 9001 |
Mazda Motor Corporation: Accessories, KD, product planning, design |
| Mazda Engineering & Technology Co., Ltd.: Specially equipped vehicles (TESMA), | ||
| etc. (Application range expanded) | ||
| Auto Alliance (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | ||
2007 |
TS 16949 |
Changan Ford Mazda Automobile Co., Ltd. (now Changan Mazda Automobile Co., Ltd.) |
| Changan Ford Mazda Engine Co., Ltd. (now Changan Ford Mazda Engine Co., Ltd.) | ||
2015 |
ISO 9001 |
Mazda de Mexico Vehicle Operation |
| Mazda Powertrain Manufacturing (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | ||
2018 |
ISO 9001: 2015 |
Mazda Motor Corporation: Head Office, Hiroshima Plant and Hofu Plant, Mazda de Mexico Vehicle Operation, |
| and Auto Alliance (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | ||
IATF16949: 2016 |
Changan Mazda Automobile Co., Ltd., | |
| Changan Ford Mazda Engine Co., Ltd. (now Changan Mazda Engine Co., Ltd.) |
Initiatives
Customer-Oriented Quality Improvement
To provide customers with satisfaction through an enriching car ownership experience, Mazda has to gain a deeper understanding of the ways in which customers use their cars and the value they expect. Mazda values customer feedback all over the globe as its greatest asset. The Company is working to store this feedback in knowledge databases, and to reflect it in product planning, development, and elsewhere. Moreover, through activities such as those to educate about or raise awareness of quality, the Company strives to continue developing personnel who think of customers as their first priority and think and act accordingly.
Understanding Customers
Activities to Turn Customer Feedback into Knowledge
Customer feedback from all over the globe are fed into a knowledge database, and Mazda is working toward vehicle development that reflects these quality criteria and optimization of product quality standards.
Sharing of Past Cases
Mazda shares the lessons learned from past cases through exhibits of actual defective products and e-learning programs in order to drive reforms in behavior.
【Statistics from FY March 2024】
・Participation in exhibits and e-learning programs by approx. 16,000 individuals


Exhibit


Participants in e-learning program
Thinking from the Customer’s Perspective
Quality Awareness-Raising Activities
Mazda holds quality meetings on a regular basis. At these meetings, top management communicate their commitment to compliance and quality in their own words to all employees. This provides opportunities for individual employees to reflect on and think about their work, thereby enhancing their compliance and quality awareness.
Quality Education
For the purpose of developing human resources capable of proactively finding and solving problems from a customer viewpoint and working for continuous improvement, quality control education is provided for employees. Quality education courses taught by internal instructors are offered, and employees take appropriate courses when their job type or management level changes.
Groupwide Quality Education Courses (FY March 2024)
| Course | Objective | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quality education program for new employees | To understand basic quality control concepts (customer-oriented attitude, continuous improvement efforts) | ||
| 2 | Quality education by level | To understand quality management approaches tailored to different management levels or job roles | ||
| 3 | Quality management methods course | To become capable of applying and practically implementing specialized quality management techniques | ||
Behavior that Puts the Customer First
Quality Control (QC) Circle Activities
Mazda promotes QC circle activities to encourage members of each workplace to find and solve problems by themselves. QC circle activities, which have been implemented for over 60 years as key activities for the Company, have evolved into global activities, being conducted not only inside Mazda but also at its suppliers and dealerships. The All-Mazda QC Circle Competition held every year at the Head Office in Hiroshima is now participated in by QC circles of Japanese dealerships and overseas sites such as those in China, Thailand, and Mexico; it is taking root as a truly global initiative.


FY March 2024 All-Mazda QC Circle Competition President’s Award
Plant Technology Department Economy Circle
Establishing Consistent Quality, from Planning to Production
To satisfy the diverse needs of customers and offer greater trust, joy, and excitement, Mazda is engaged in establishing a consistent quality level to be assured at all stages from planning and product development to the delivery of products to customers.
Consistent Quality from Planning to Production
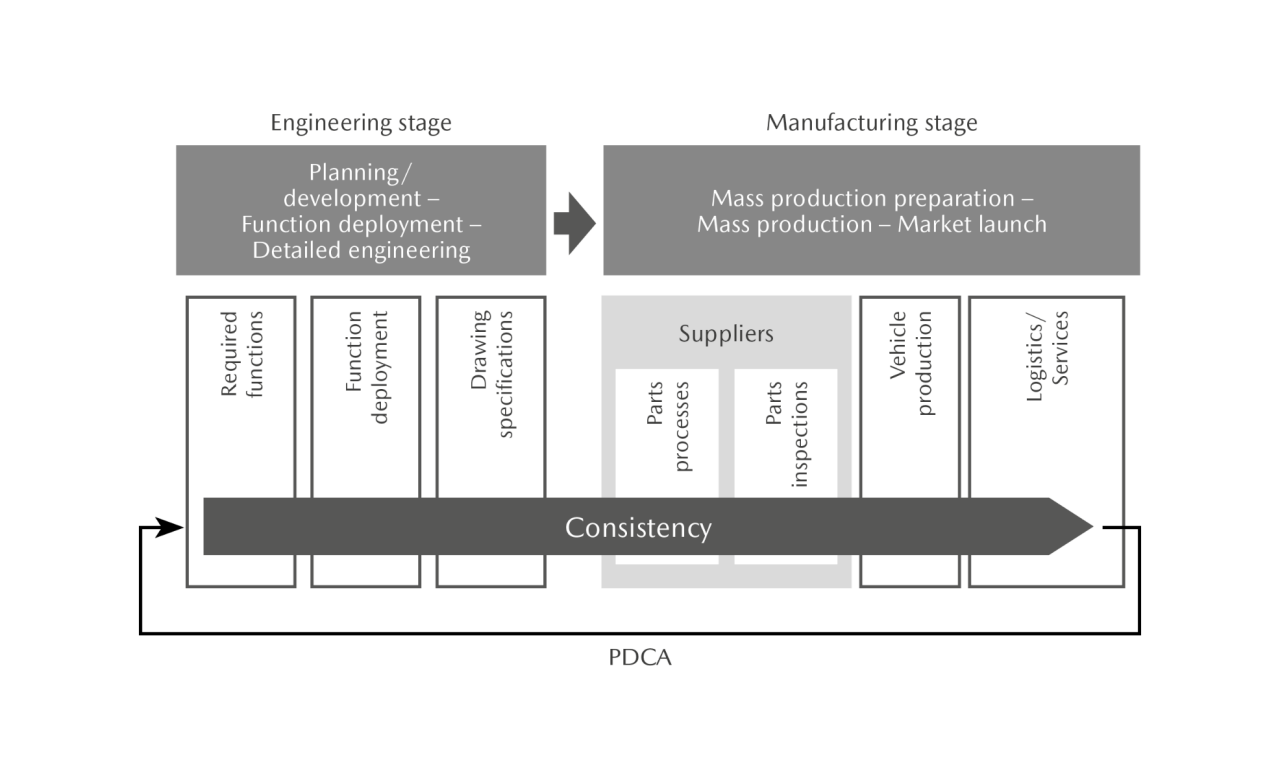
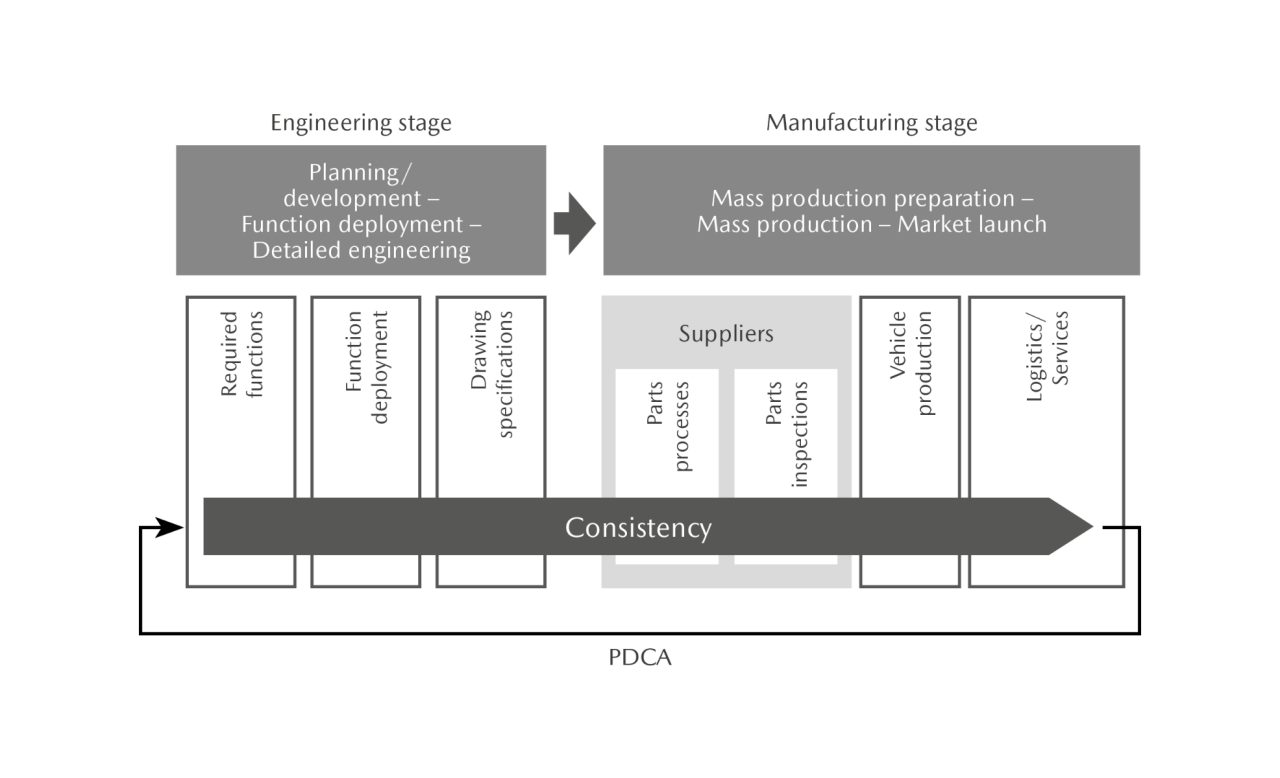
Mazda is committed to process assurance to improve the performance of products as well as to enhance the quality of new technologies in response to regulation and electrification trends. Process assurance is the approach of ensuring a consistent quality level at all stages spanning from engineering (planning and product development) to product creation (purchasing, vehicle production, logistics, and after-sales services). Through this approach, the Company identifies the important elements necessary to guarantee the quality of each function and performance based on an accurate understanding of customer needs and expectations. The Company has established a system to maintain and manage these elements in every stage from engineering to manufacturing. The cooperation of partners is imperative in improving quality levels. For this reason, the Company promotes personnel and technology exchanges as well as other co-creation activities with customers. Furthermore, to allow customers to feel the joy of driving through its products, the Company identifies the functions and performance that embody the joy of driving for each stage from before getting in the car to after starting driving, so as to achieve increased consistency in quality.
Consistent Process Assurance Based on Major Characteristics
Monotsukuri Innovation
Looking five to 10 years into the future, Mazda has implemented Monotsukuri Innovation for efficiently developing and manufacturing products. Shared development methods and manufacturing processes are made possible by using bundled product planning for models to be introduced in the future through an approach that transcends the boundaries of market segments and model classes.
During the development phase, optimized structures for each function are shared among vehicle models and classes to apply these structures to a wider range of vehicles. In the production phase, Mazda’s unique flexible production system is used to produce products engineered based on a common architecture concept in a highly efficient and flexible manner. Mazda is aiming to raise operational efficiency by building flexible production frameworks that can handle changes in volumes and can quickly introduce new models with a minimum of investment. Through Monotsukuri Innovation, the Company has achieved efficiency improvement in terms of both product development and manufacturing facility investment as well as significant improvements in vehicle costs in relation to Skyactiv Technology and products after and including the CX-5 launched in 2012.
Through design based on common architecture under Monotsukuri Innovation, Mazda is able to promptly apply the latest technologies and designs to all of its products. In new-generation technology development, the Company is working to enhance the efficiency of development processes through bundled planning and model-based development.
Model-Based Development
Cars are being called on to provide increasingly advanced and diverse functions, while vehicle architecture and control systems are becoming more and more complex. Model-based development, which uses computers to efficiently replicate development processes, is essential to keep developing complex systems quickly and with limited resources. Model-based development involves creating computer models of the vehicle, control systems, drivers, passengers, driving environments, and other development subjects and conducting development via thorough computer simulation. It is an efficient method of optimization. Mazda is carrying out model-based powertrain and vehicle development through simulations for stages spanning from design to vehicle evaluation. The Company thereby strives to reduce the number of prototype parts and actual unit verification in order to develop complex, highly sophisticated technologies and products quickly and with minimum resources while also ensuring quality.
Mazda believes that to further promote model-based development, universities working on cutting-edge technologies and automobile manufacturers and suppliers that cooperate in manufacturing must build upon the SURIAWASE 2.0 concept, which is aimed at enhancing development efficiency by using virtual models across the engineering chain. To that end, the Company is playing an active role in activities by the Japan Automotive Model-Based Engineering center (JAMBE). To spread the SURIAWASE 2.0 concept throughout the Japanese automotive industry, the Company is engaging with domestic automobile manufacturers and business partners.
Model-Based Development
A technique to develop outstanding products by modeling (quantifying) and connecting all four elements of (1) the car, (2) control systems, (3) the driver & passengers, and (4) the driving environment without using an actual vehicle
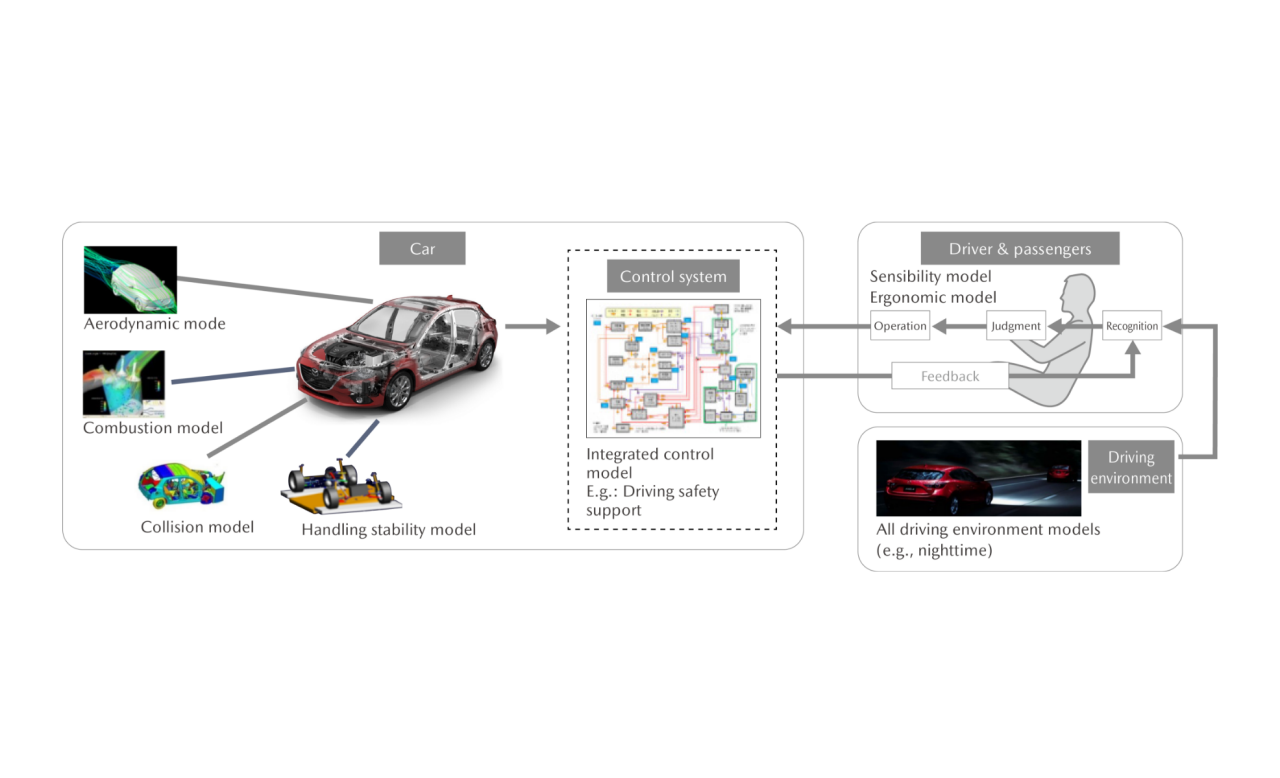
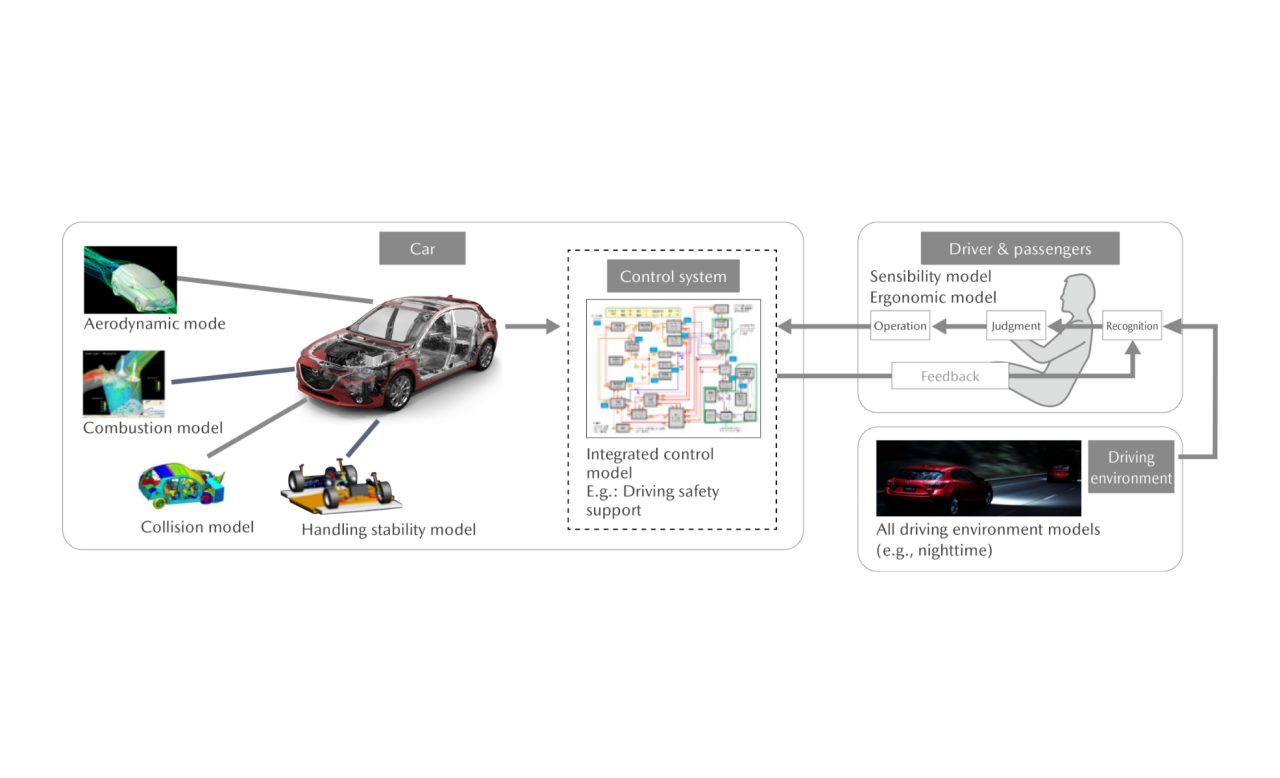
What Is Advanced Matching Development SURIAWASE 2.0?
Created based on the SURIAWASE 2.0 concept presented in the materials prepared by Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry in 2017
SURIAWASE 2.0 is an initiative to enable academia and businesses (parts manufacturers and OEMs of all sizes) to share digital models across the board, linking academic research with development of parts, systems, and vehicles, thereby allowing both sides to coordinate and make adjustments (“Suriawase” in Japanese) digitally from the initial stages of development, without using physical machines. This approach makes it possible to create the most advanced development community in the mobility sector, able to carry out optimal and high-grade monozukuri (engineering and manufacturing) efficiently and without rework.
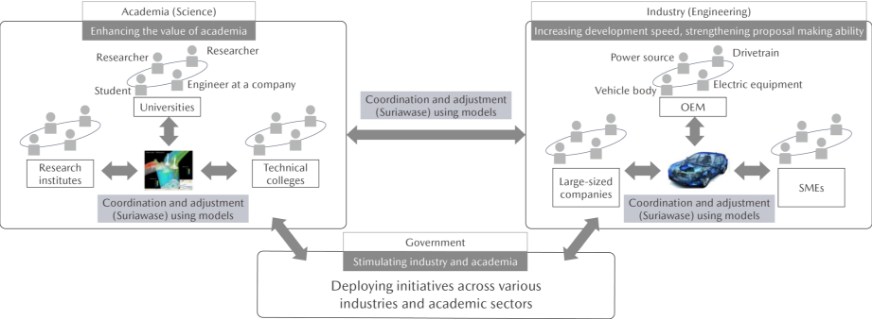
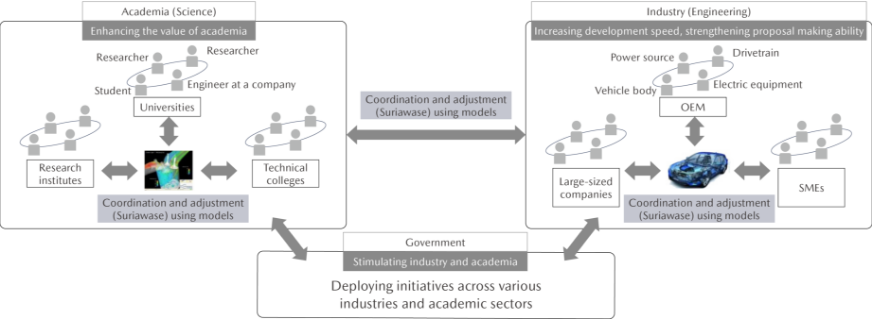
Goal: Concretize SURIAWASE 2.0
Achieve the most efficient development processes in the world and create new value by innovating the research, development, and production processes
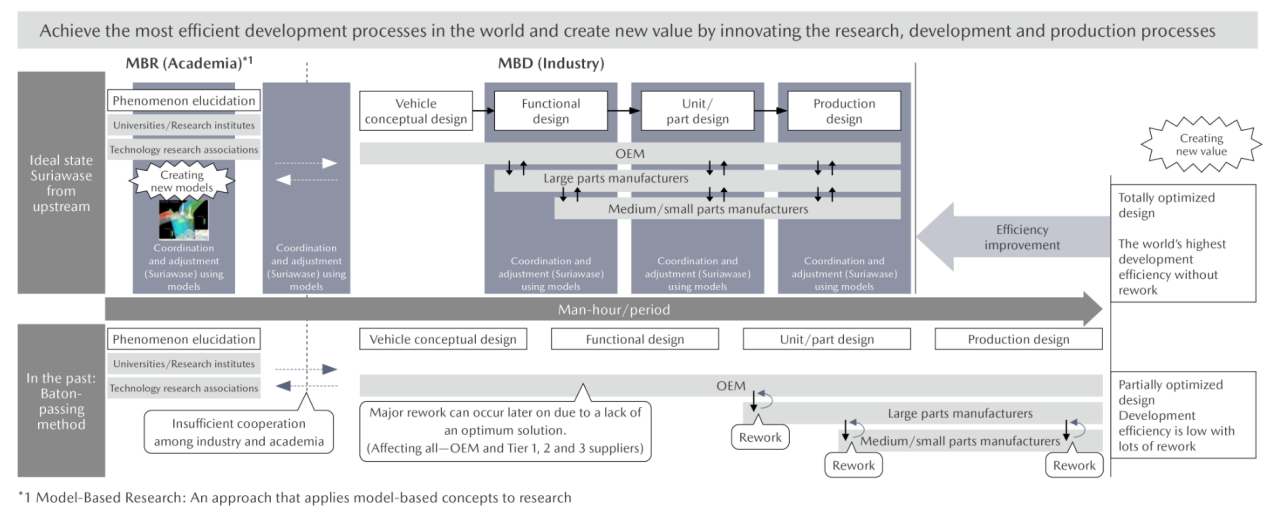
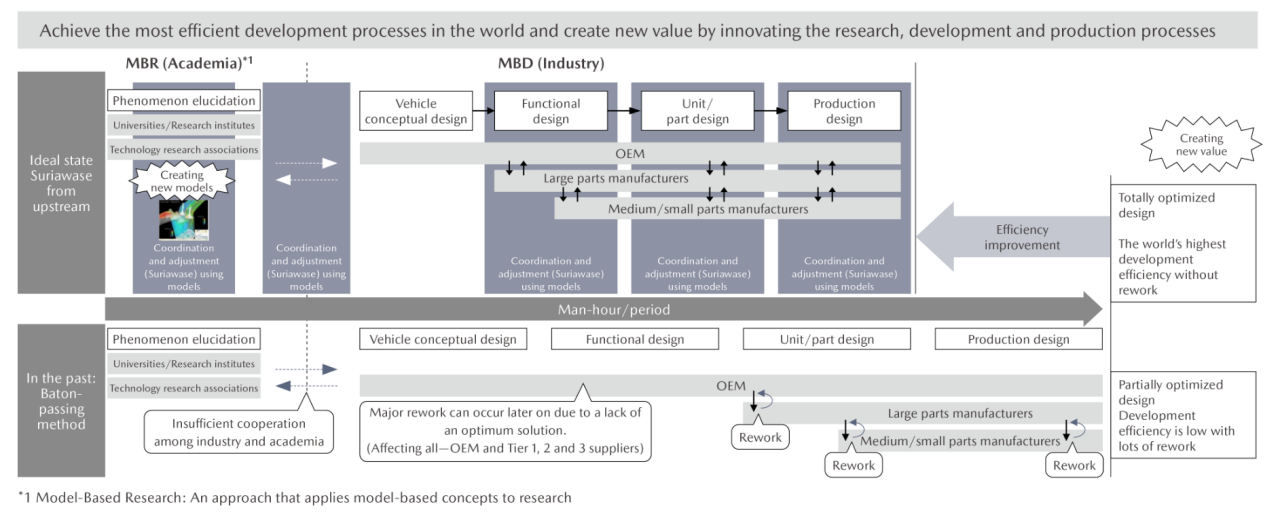
Referred to the October 2022 issue of “Introduction to JAMBE"
Early Detection and Early Solution of Market Problems
Mazda strives to offer an enriched car ownership experience in which customers can feel satisfied with their car and realize its value as a product. While respecting each vehicle as a certain customer’s one-and-only, the Company endeavors to ensure comprehensive and speedy quality improvement and enhance the quality of present and future products.
Comprehensive and Speedy Quality Improvement
To ensure early detection and early solution of market problems, Mazda has established a system for unified management of all items of quality information. Such information is gathered from distributors and dealerships in Japan and overseas and by employing the results of surveys by external institutions and conducting the Company’s own market research. Through the system, the collected information is shared Companywide in real time. By using the system and closely monitoring daily progress, the Company investigates quality-related incidents and their causes, determines and implements improvement measures, and confirms the results. In this manner, the Company works to achieve comprehensive and speedy improvement. The Company also carries out quality improvements capitalizing on the vehicle information collected through the utilization of connectivity technologies in addition to conventional initiatives based on customer input.
Quality Improvement System
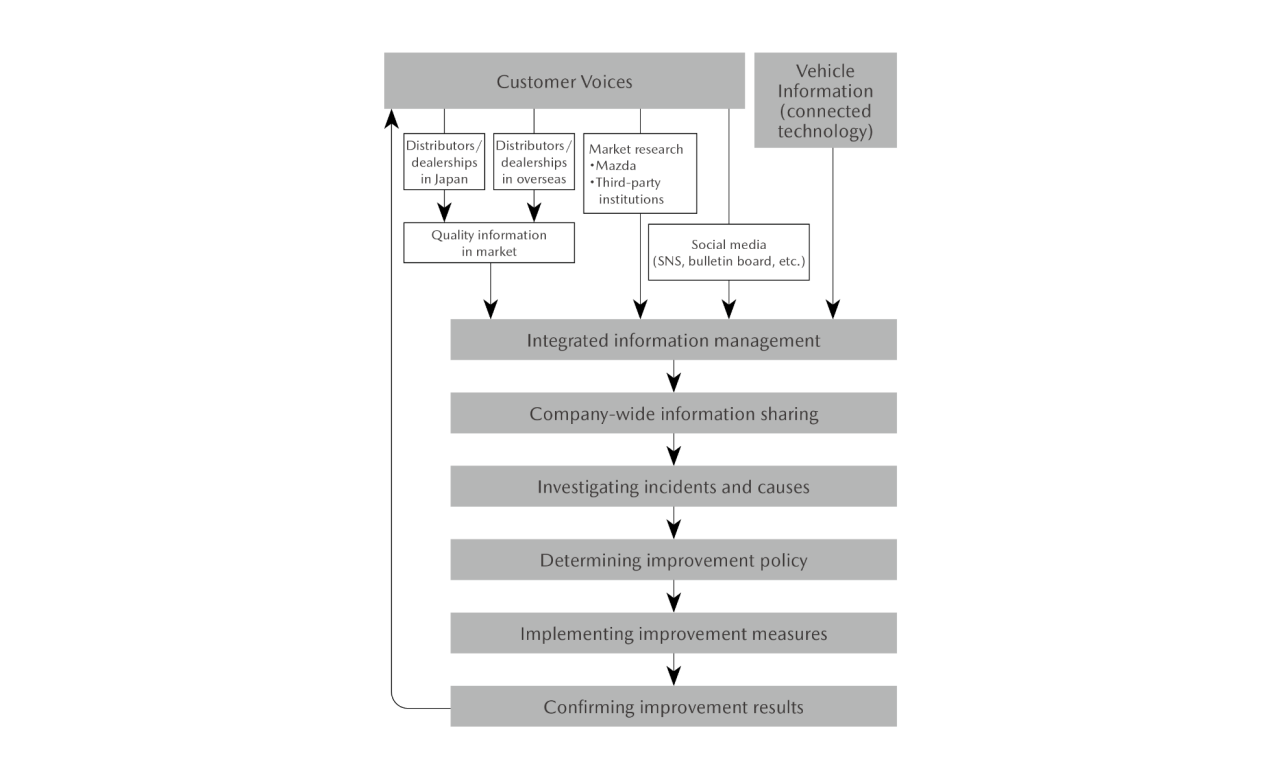
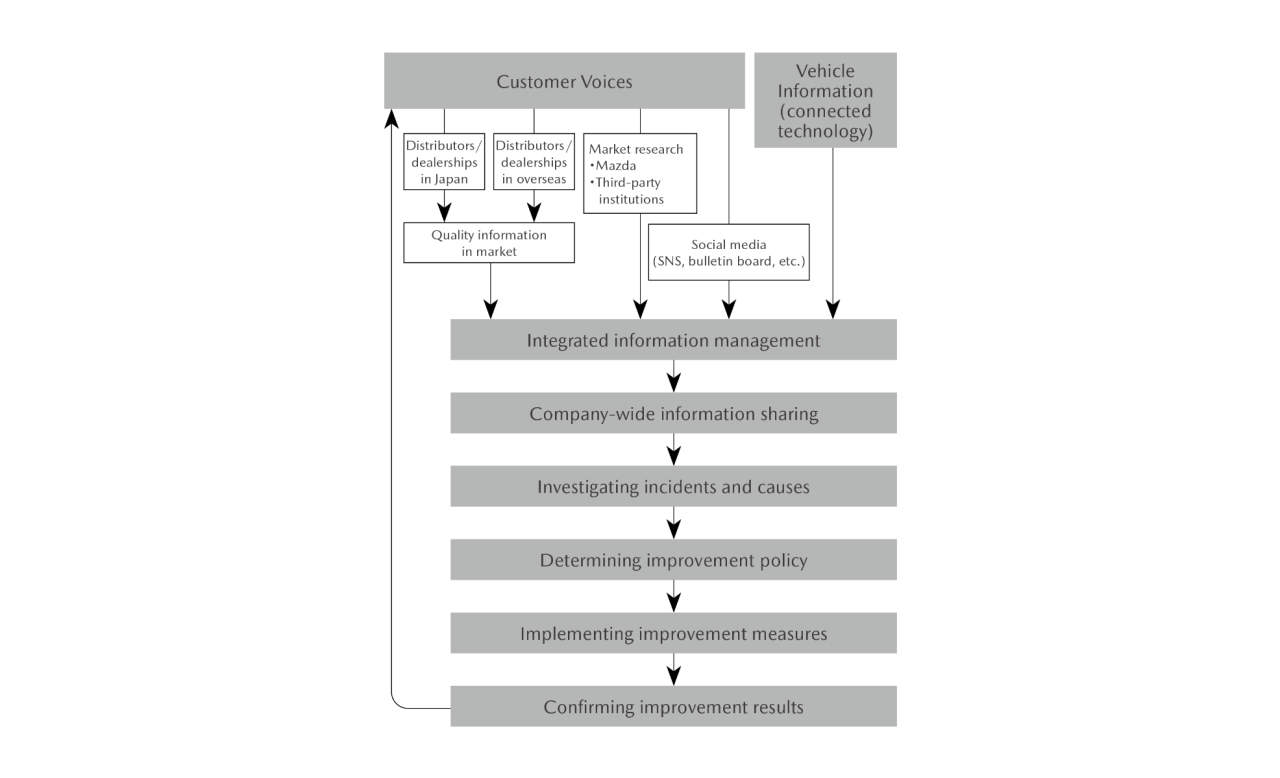
【Examples of Surveys, Analyses, and Improvement Measures 】
- Gathering customer feedback through Mazda-unique market surveys
- Market surveys conducted by third parties
- Analysis of customer feedback via social media
- Analysis of vehicle information obtained through connected technologies
Customer Safety and Security as Highest Priority for Corporate Activities
Mazda prioritizes customer safety and security above all. Through a strict quality assurance system, the Company conducts inspections on conformity with laws and regulations of relevant countries and on functions to be used by customers with a view to manufacturing vehicles that customers feel safe using. This quality assurance system is maintained and managed by having development, production, and quality divisions audit each other from their respective independent standpoints.
Recall Procedures (Overview)*
- Registration with authorities in each jurisdiction in accordance with the laws and regulations of each country and region
- Disclosure to customers via direct mail, telephone, and other methods and explanations at dealerships
- Disclosure of information on recalls on the Mazda website
Social data (Number of recalls in Japan)
* Recall procedures may vary by country or region.
Building an Emotional Connection with Customers
Customer Support Tailored to Customer Needs
Mazda aims to provide customer service that customers can always rely on. To this end, in addition to providing safe, reliable, and comfortable vehicles, Mazda also provides a stress-free ownership experience that allows customers to enjoy their vehicle-related lifestyle, including visits to dealerships. Understanding customers’ difficulties and expectations is crucial to successfully tackling this challenge. In addition to the fundamental efforts to develop and provide tools and service manuals and to establish parts supply networks, the Company is working with dealerships in Japan and overseas to reform operations, create new touch points with customers, and cultivate human resources capable of considering and acting toward customers’ happiness.
Tools & Service Manuals |
・ Establishing an internet-based support system that enables quick and efficient access to the latest service manuals as well as efficient searching for and ordering of parts ・ Deploying unique malfunction diagnostic devices that are compatible with the sophisticated electronic control systems adopted in a wide range of safety and environmental technologies
・Providing information on special tools dedicated to Mazda vehicles and their usage |
Development of Dealership Sales Staff |
・Positioning of instructors in training centers in major countries and regions of operation; incorporating development and production innovations into new machinery and technical training to develop human resources globally; and proactively utilizing remote training tools to satisfy the needs of those requiring training and improve training efficiency
・Holding global events to recognize service maintenance technicians who represent their respective countries and service staff members who help supply customers with enriched car ownership experiences to foster individual growth, motivation, and pride among employees |
Initiatives at Dealerships and Distributors
Mazda is committed to providing dealership and distributor experiences that accommodate the needs of individual customers. The Company therefore promotes operational improvement measures driven by dealerships and distributors with the aim of heightening process quality and creating more comfortable work environments for employees. The Mazda Production System, which is built on Mazda’s accumulated production insight, is a central component of these initiatives. Through initiatives involving all dealership and distributor employees, the Company seeks to eliminate operational inefficiencies while increasing the value of processes from the perspective of the customer. In FY March 2024, the Company expanded the scope of dealerships and distributors in which improvements are pursued to include those located overseas in addition to those in Japan. To enhance the level of customer satisfaction initiatives at Mazda dealerships and distributors, the Company has prepared award systems for sharing and honoring best practices demonstrated by the staff of dealerships and distributors that have contributed to increased customer satisfaction through excellent teamwork and the sales and service staff members who achieved outstanding results.
Staff Awards & Shop Awards
| Measure | Frequency | Objective/Contents | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Staff Awards/ Shop Awards |
Once a Year |
To encourage staff self-improvement, meetings are held on a periodic basis to award sales and service staff members according to their degrees of achievement of targets. Improvement of technical skills, and contribution to improved vehicle quality. Awards are also given to dealerships that have achieved their targets as a result of all staff members' customer-oriented activities, demonstrating excellent teamwork. In particular, best practices from the shops producing outstanding results are shared and commended at the presentation meetings hosted by the Mazda Dealerships Association each region across Japan. |
|||||||||||||
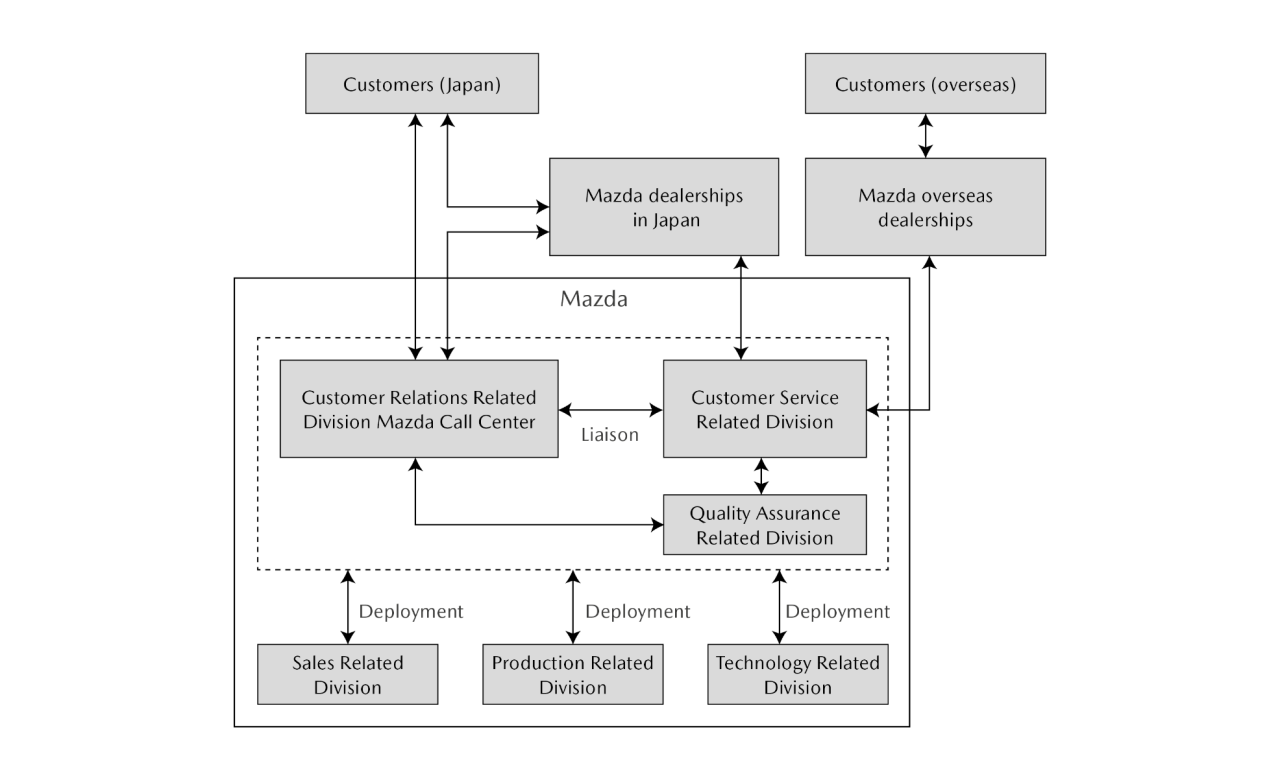
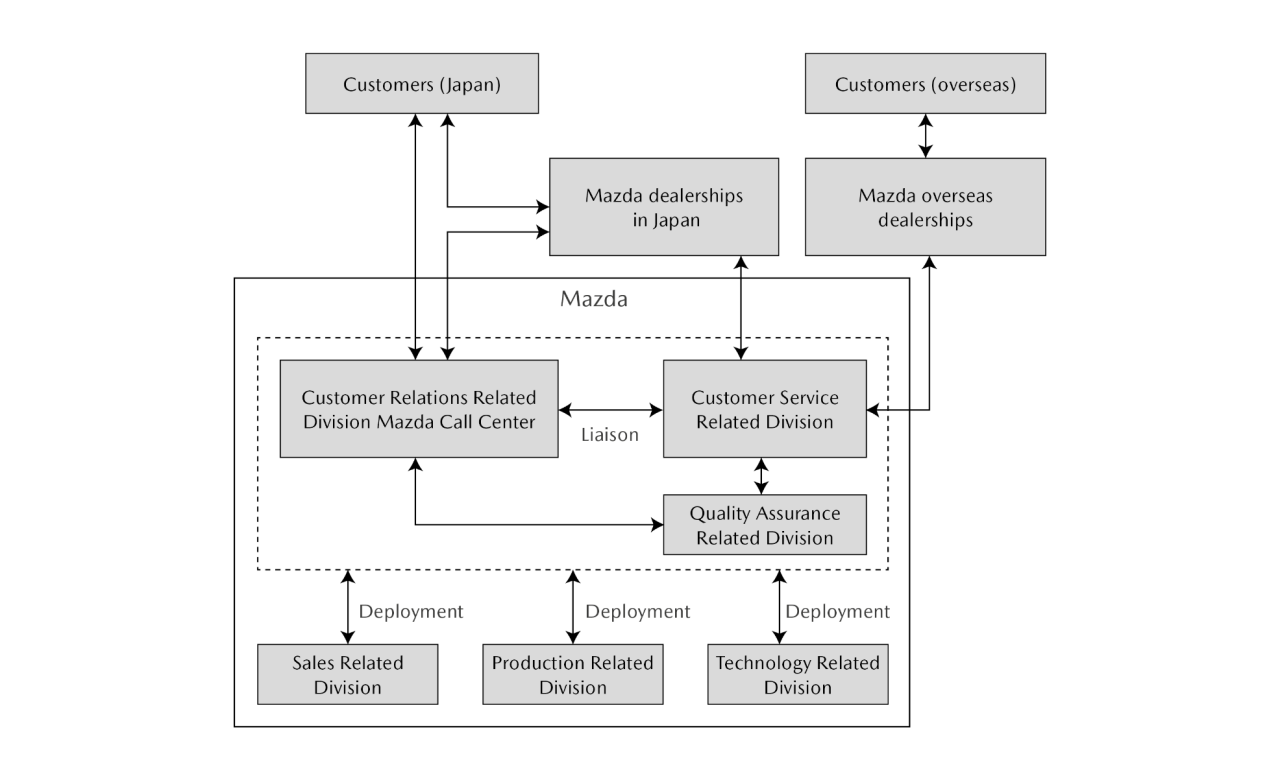
Responses to Expectations and Opinions of Customers
At Mazda dealerships and distributors around the world, systems have been established to gather opinions and requests from customers, to respond to them honestly, accurately, and quickly, and to reflect this input in sales and services in cooperation with the Mazda Head Office.*1 The contacts for each market area as well as an FAQ section*2 are available on Mazda's corporate website for the convenience of customers. To strengthen bonds with customers, Mazda conducts global surveys focusing on the Mazda brand experience, sales and after-sales services, ownership cost, product attractiveness, and other specific items. Through these surveys, the Company identifies problems in each market and addresses them in cooperation with local dealerships and distributors. Having defined indicators to measure customer satisfaction, the Company is implementing a plan–do–check–act (PDCA) cycle to improve customer satisfaction.
*1 Distributor list by country/region
*2 Inquiries from Japan/FAQ (in Japanese only)
Framework