The operating environment for the automotive industry continues to grow increasingly competitive due to stricter environmental and safety regulations, new competitors from other industries, and the diversification of the mobility business. In the face of this competition, Mazda is accelerating its efforts to engage in collaboration with partners through open innovation with companies, universities, and government agencies as it seeks to form relationships with allies in the automotive and other industries. We thereby aim to drive the ongoing growth and development of the Mazda Group while exercising our corporate philosophy and contributing to society.
OPEN INNOVATION (EXPLORATION OF PARTNERSHIPS FOR CO-CREATION WITH OTHERS)
Basic Approach
Objectives of Open Innovation
【Growth of the Mazda Group】
- Improve engineering capabilities, enhance the brand value, and increase R&D efficiency
【Contribution to Society】
- Contribute to the development of a sustainable society, advance Monozukuri (engineering and manufacturing) and share related knowledge and skills, and drive the development of regional economies
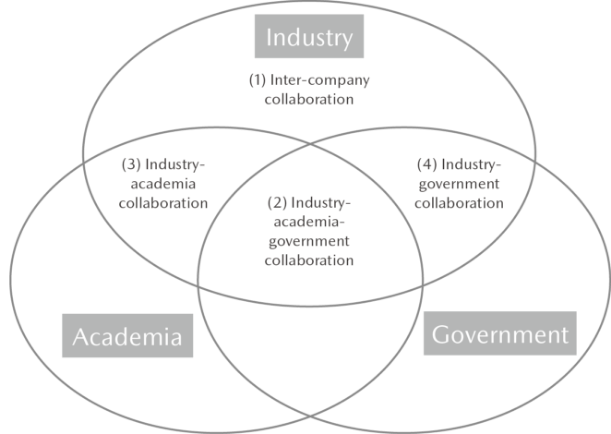

- Inter-company collaboration
Collaboration with automobile manufacturers, suppliers, and other partners - Industry-academia-government collaboration
Collaboration with local governments and companies (Hiroshima Council of Automotive Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration*) - Industry-academia collaboration
Joint research with universities, collaboration with government institutions and research institutions (participation in national projects) - Industry-government collaboration
Participation in technology exhibitions organized by government authorities (communication of information on needs and seed technologies)
* The Hiroshima Council of Automotive Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration is a council that promotes industry–academia–government collaboration. Motivated by a strong desire and enthusiasm for development of the manufacturing industry in Hiroshima, its member organizations have voluntarily joined the council to examine the ideal form for the manufacturing industry and to leverage innovation to spur industrial development.
Initiatives
Mazda is establishing value co-creation bases for use in industry-academia-government collaboration and empowering human resources in order to facilitate co-creation that extends beyond the boundaries of automobiles. This approach is taken in reflection of the need for the development and innovation of software technologies in light of the trends toward carbon neutrality and electrification.
Mazda R&D Center Tokyo
The Mazda R&D Center Tokyo was opened in July 2025 as part of the Company's efforts to strengthen its presence and capabilities in the Tokyo metropolitan area. This facility will augment Mazda's software development capabilities to enable more agile responses to the shift toward intelligent vehicles. To this end, the center offers an environment where software engineers can work comfortably, supports enhanced recruitment efforts, and promotes co-creation with universities, companies, and research institutions in the Tokyo metropolitan area.
【Related Article (News Release)】
Mazda to Open 'Mazda R&D Center Tokyo' in Azabudai Hills, Relocating Its Tokyo Office
Inter-Company Collaboration
Mazda has been promoting inter-company collaboration with other automobile manufacturers, suppliers, and other partners to enhance their manufacturing and engineering capabilities and create synergies.
Collaboration with Partners
By working together with its partners to pursue shared aspirations, while incorporating external insight to address social issues affecting the automotive industry and contributing to the ongoing growth of society and companies, Mazda aims to be a company that partners feel attached and have a sense of pride in their connection. We thereby want to make Mazda a brand that is connected to all stakeholders, including customers, by the strongest of bonds. The Company plans to promote active collaboration founded on mutual trust with various other companies.
【Recent Examples of Collaboration】
Support for the Autonomous Growth of Local Suppliers
Mazda has continued to implement the Autonomy Development program with a focus on suppliers that had joined the Company in advancing the Jiba Achieve Best Cost (J-ABC) program for collaborative improvement activities together with local suppliers. The Autonomy Development program is designed to foster a deeper understanding of the Mazda Production System (MPS) to support the construction of human resource development systems at suppliers. Specifically, we provide suppliers with four rank-based training programs—senior manager training, promoter training, management training, and supervisor training—to disseminate understanding of MPS principles and frameworks at production sites. Individuals who have completed the supervisor training programs are dubbed Master Trainers and entrusted with the responsibility of training future supervisors at suppliers. In FY March 2025, we began devoting attention to new initiatives that spread beyond the boundaries of prior training programs to support the development of human resources in accordance with supplier needs and communicate the joy of manufacturing to younger individuals. Through these initiatives, we hope to establish cycles for the ongoing and autonomous development of human resources at suppliers and to contribute to enhancements to the capabilities and motivation of the people who interface with customers at the front lines of operations. Mazda is committed to continuous effort to grow with suppliers and build frameworks that allow both partners to engage in sustainable manufacturing.
【Statistics from FY March 2025】
- Implementation of MPS at a total of 25 suppliers in Japan
- Appointment of 28 MPS Master Trainers at 12 suppliers
Vision for Promotion of MPS


MPS Flow Chart


Program Developed for Local Suppliers


Implementation of the Autonomy Development Program at Overseas Production Sites and Local Suppliers
In tandem with the transition to the Autonomy Development program in Japan, the Company has begun introducing the Global Manufacturing Network (GMN) at overseas production sites to support the autonomous growth of local suppliers. The GMN is being implemented at five overseas production sites: AutoAlliance (Thailand) Co., Ltd.; Mazda Powertrain Manufacturing (Thailand) Co., Ltd.; Changan Mazda Automobile Co., Ltd.; Changan Mazda Engine Co., Ltd.; and Mazda de Mexico Vehicle Operation.
【Statistics from FY March 2025】
- Implementation of GMN at a total of 25 suppliers overseas
- Appointment of 34 MPS Master Trainers at 25 suppliers
Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration
Mazda, having established the Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration Secretariat, is ramping up collaboration with local companies, universities, and government agencies. Through collaboration among industry, academia, and government, the Company is contributing to local communities in terms of developing new creative technologies and fostering human resources capable of bringing about innovation.
Hiroshima Council of Automotive Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration
With its R&D and production facilities mainly positioned in Hiroshima Prefecture, Mazda is working through the Hiroshima Council of Automotive Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration to collaborate with the Chugoku Bureau of Economy, Trade and Industry, Hiroshima Prefecture, Hiroshima City, the Hiroshima Industrial Promotion Organization, and Hiroshima University to advance research and development of next-generation technologies, support local automobile-related companies, and contribute to the invigoration of the region and its economy. Moreover, we are working toward the achievement of the 2030 Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration Vision established in 2015. To this end, various activities are being conducted, such as the creation of new frameworks to support local businesses, investigation of next-generation automotive societies, and raising of awareness across society. Following its selection for a subsidy under the Cabinet Office's Project for Revitalization of Local Universities and Regional Industries* for FY March 2019, Mazda was chosen in FY March 2024 for additional support to further expand upon its original activities. This led Mazda to establish the Digital Monozukuri Education Research Center at Hiroshima University, where it has been conducting R&D activities related to innovative materials technologies, data-driven control technologies, smart inspection monitoring, and smart battery and air-conditioning systems. We will continue to accelerate activities with a view to the social implementation of development technologies in the future.
* Under this project, the Hiroshima Prefecture Special Committee to Promote the Project for Revitalization of Local Universities and Regional Industries (Chairperson: Hidehiko Yuzaki, Governor of Hiroshima Prefecture; Project manager: Kiyotaka Shobuda, Representative Director and Chairman of the Board of Mazda Motor Corporation) was established.
Hiroshima Council of Automotive Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration's 2030 Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration Vision
- Transform Hiroshima into a hub that attracts people seeking innovative automotive technologies and dynamic car culture and a place that continually produces technologies that amaze the world
- Nurture human resources capable of innovation across all generations and enliven the region through Monozukuri (engineering and manufacturing) via industry–academia–government collaboration
- Develop Hiroshima's unique approach toward industry–academia–government collaboration into a leading model for regional development in Japan that can also serve as a benchmark for the rest of the world
Major Initiatives
| Initiatives | Details |
|---|---|
| Support for programming education at elementary schools | Support for programming education at elementary schools in Hiroshima Prefecture following a curriculum designed under the guidance of the Hiroshima Council of Automotive Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration and using videos and car-shaped robots as part of efforts to foster human resources capable of bringing about innovation |
| Co-creation and technology exchanges with suppliers |
|
| Popularization and use expansion of next-generation liquid fuel |
|
| Fundamental research to support model-based development* of vehicle power sources |
|
| Deployment of manufacturing approach in kansei (sensibility) field and development of human resources with related expertise |
|
| Human resources development in model-based development field | Organization of basic courses for development of human resources with model-based development and computer-aided engineering skills for automobile suppliers and manufacturing companies in collaboration with the Hiroshima Digital Innovation Center to enhance the R&D capabilities of local companies |
* Model-based development is a development process employing simulation technologies.
Promotion of Model Distribution for the Automotive Industry
Mazda has participated in the Study Group for Ideal Approaches to Model Utilization in the Automobile Industry organized by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry since its launch in November 2015. In this capacity, the Company takes part in initiatives with other automobile and parts manufacturers to spread model-based development.
In April 2018, the Company expressed its agreement with Enrichment of SURIAWASE 2.0 for the Automobile Industry (an industry-academia-government joint strategy project policy), and announced that the Company would continue with initiatives for evolving model-based development approaches and expanding the scope of coordination. In addition, Mazda formulated the guidelines for smoothly promoting model distribution between companies, based on the results of activities implemented by the study group thus far. In December 2018, the study group and ProSTEP iVip,*1 an international standardization preparatory organization, and the digital transformation promotion organization SystemX*2 jointly announced these guidelines to the world as international rules originating from Japan. This study group concluded its activities in March 2021, and the Japan Automotive Model-Based Engineering center (JAMBE) was established in September 2021 to carry on its activities by promoting the widespread use of model-based development technology throughout the Japanese automotive industry. At the time of its establishment, 10 private-sector companies became operating members of JAMBE. In March 2023, the organization was made a general incorporated association. Mazda is also participating as one of the operating member companies and takes full advantage of the virtual simulation and unique model-based development knowledge that has been accumulated through Mazda Digital Innovation to contribute to activities for increasing the global competitiveness of the Japanese automobile industry.
【Statistics from FY March 2025】
- JAMBE membership of 187 companies and organizations as of March 31, 2025
*1 ProSTEP iVip is an international standardization organization based in Germany. Its membership comprises 185 companies, primarily automobile manufacturers in Europe, the United States, and Japan, as well as airlines and software companies. ProSTEP iVip works to develop and promote international rules regarding computer-aided design and model-based development.
*2 SystemX is a digital transformation research organization based in France.
SURIAWASE 2.0
SURIAWASE 2.0 is a scheme formulated by the Study Group for Ideal Approaches to Model Utilization in the Automobile Industry organized in November 2015 by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry to further improve the international competitiveness of Japan's automotive industry. This scheme calls for the enhancement of development coordination processes between companies across Japan's supply chain by taking advantage of a model-based development approach that uses virtual simulations instead of physical machines.
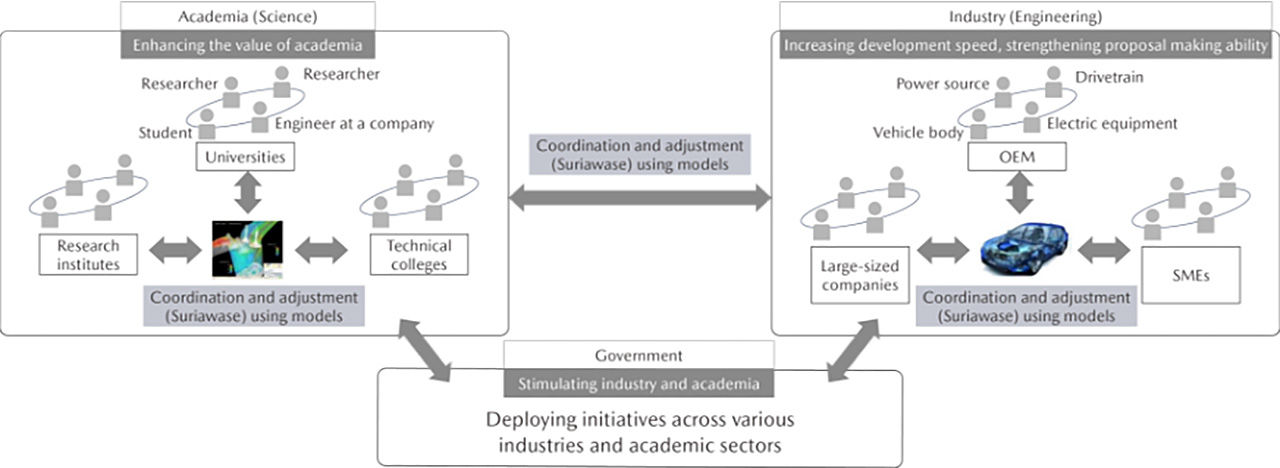

Vision for Implementation of SURIAWASE 2.0
Through the implementation of SURIAWASE 2.0, Mazda aims to achieve the most efficient development processes in the world and create new value by innovating the research, development, and production processes.
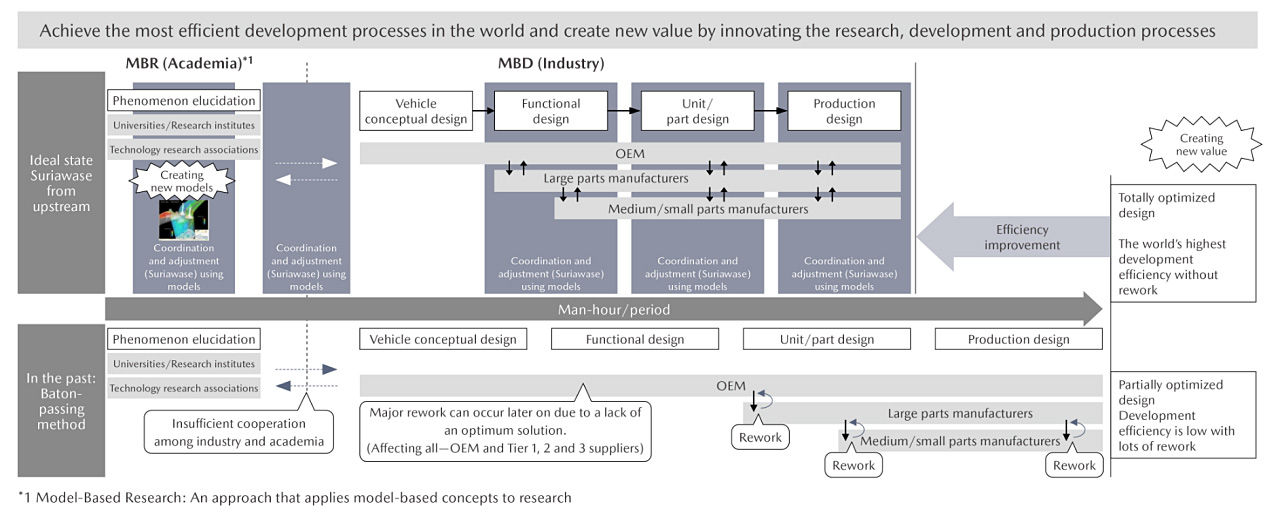

For more information, please refer to the October 2022 issue of "Introduction to JAMBE."
Research on Microalgae through Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration
Mazda has turned its attention to the mass cultivation of microalgae and is advancing research on this subject with the aim of achieving mass production of next-generation biofuels. Microalgae boast a high production capacity when compared with vegetable resources, which are used to produce edible oils.
- 2017: Launched a joint research course called the Next-generation Automotive Technology Joint Research Course—Algae Energy Creation Laboratory at a graduate school of Hiroshima University
- 2020: Joined the Institute of Microalgae Technology, Japan
- 2021: Commenced an ongoing research project looking at improving algae performance using genome editing technology in collaboration with Hiroshima University and Tokyo Institute of Technology and with support from the Program on Open Innovation Platform for Industry-Academia Co-Creation sponsored by the Japan Science and Technology Agency
- 2022: Joined Microalgae Towards Sustainable & Resilient Industry, a consortium whose projects have been selected for support by the NEDO Green Innovation Fund
【Related Information (Sustainability Website)】
Basic and Applied Research on Technologies for Internal Combustion Engines and Cleaner Exhaust Emissions
Mazda participates in the Research Association of Automobile Internal Combustion Engines (AICE),* an organization that promotes joint research in the Japanese automotive industry through collaboration between industry, academia, and government. AICE is advancing research projects based on research scenarios aimed at achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 and is being funded by subsidies from the Japanese government's Green Innovation Fund. Through its involvement in AICE, Mazda is working to resolve common technological issues via coordination with universities and other automobile manufacturers. One part of our Multi-Solution Strategy, these activities are aimed at achieving carbon neutrality and zero emissions for internal combustion engines with an eye toward using carbon-neutral fuel.
* AICE is a technical research union established in April 2014 with the certification of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. This organization is designed to enable automobile manufacturers to conduct basic and applied studies jointly with universities and research institutions on themes common to automobile manufacturers and to use the research results to accelerate their in-house development activities.
Industry-Academia Collaboration
Mazda has implemented frameworks for efficiently advancing research and development through collaboration with universities and other educational institutions and research institutions.
Participation in World-Leading National Projects and Joint Studies with Research Institutions
Mazda participates in world-leading national projects and joint studies with external research institutions with the aim of resolving social issues facing the automotive industry.
| Relevant Government Agencies/Institutions | Project Name |
|---|---|
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), NEDO Green Innovation Funding Program Coordination Office | Green Innovation Fund Projects/Development of Next-Generation Batteries and Next-Generation Motors (in Japanese only) |
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, NEDO, Energy Conservation Technology Department of NEDO | Program to Develop and Promote the Commercialization of Energy Conservation Technologies to Realize a Decarbonized Society (in Japanese only) |
| Cabinet Office, Regional Development Bureau | Local University and Industry Grant Program for Digital Transformation of Hiroshima's Manufacturing Industry (in Japanese only) |
Collaboration with Universities
By enhancing collaboration with universities in various fields, Mazda aims to help address a broader range of issues from a wider perspective and to thereby contribute to society.
| University | Outline of Collaboration |
|---|---|
| Hiroshima University |
|
|
|
|
|
| Hiroshima City University |
|
| Kyushu University |
|
|
|
| Kindai University |
|
| University of Hyogo |
|
| Tokyo Institute of Technology |
|
|
|
| University of Tokyo |
|
| Hirosaki University |
|