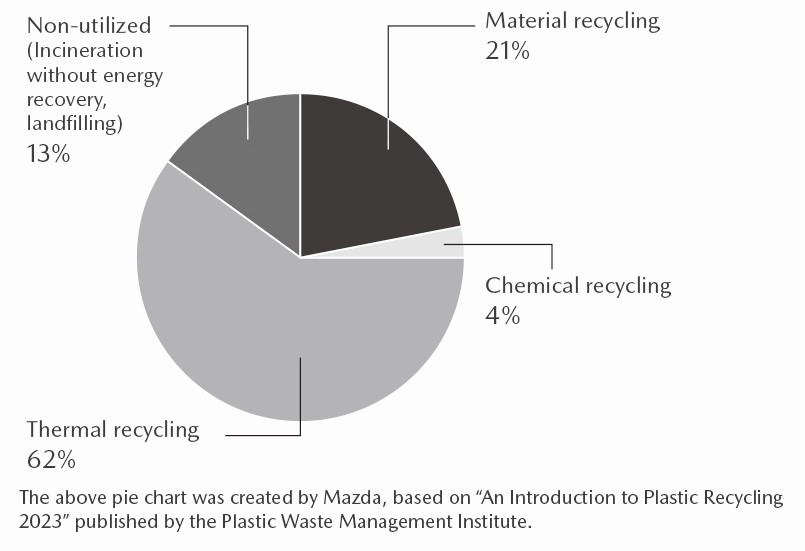
In conjunction with global population growth, the international community is facing challenges due to an increase in demand for resources and even more serious environmental issues, including the rising amount of waste. To address these challenges, it is necessary to transition to a circular economy that considers medium- and long-term outlooks, and also to promote the conventional 3R (reduce, reuse, and recycle) initiatives in all economic activities. A circular economy involves generating new value while reducing resource inputs and consumption and making effective use of resource stocks. Plastic recycling is indispensable in achieving a circular economy. In Japan, currently an estimated 60% of plastic waste goes through thermal recycling, which means that the waste is combusted in incinerators to produce energy. In Western countries, however, combustion generally is not considered a form of recycling. Also, a minute amount of dioxin is generated during the process of combustion. For these reasons, companies are expected to contribute to the circular use of resources (material recycling and chemical recycling) or to use biomass plastics.