INITIATIVES TO ADDRESS ISSUES RELATED TO THE EARTH: PROMOTING RESOURCE CIRCULATION
Sustainable Development Goals


Relevant SDGs Targets
6.3 Improve water quality through various measures.
9.4 Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
12.4 Achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes, and significantly reduce their release in the air, water, and soil.
12.5 Substantially reduce waste generation.
Social Issues
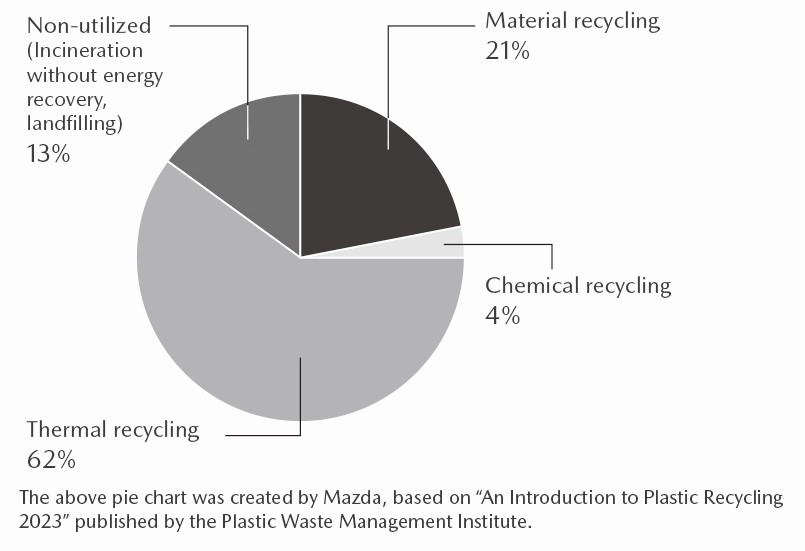
In conjunction with global population growth, the international community is facing challenges due to an increase in demand for resources and ever more serious environmental issues, including the rising amount of waste. To address these challenges, it is necessary to promote the 3Rs (reduce, reuse, and recycle) across all economic activities and to transition to a circular economy over the medium to long term. A circular economy involves generating new value while reducing resource inputs and consumption and making effective use of resource stocks. Plastic recycling is indispensable in achieving a circular economy. In Japan, currently an estimated 60% of plastic waste goes through thermal recycling, which involves combusting waste in incinerators to produce energy. In Western countries, however, combustion generally is not considered a form of recycling. Also, a minute amount of dioxin is generated during the process of combustion. For these reasons, there is a call for companies to contribute to the circular use of resources (material recycling and chemical recycling) or to use biomass plastics.
Breakdown of Plastic Waste Recycling by Method (Japan)

Resource Circulation (Water)
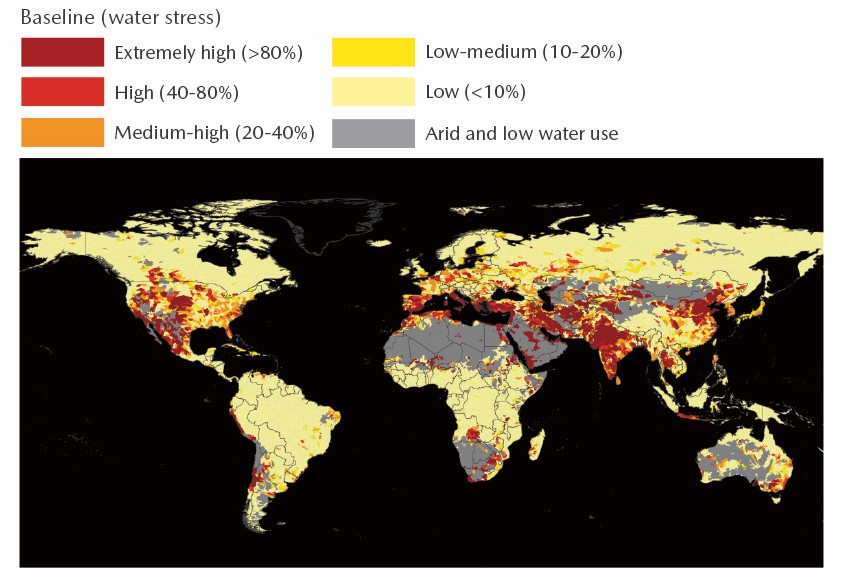
Of the total volume of water existing on the earth, only 0.01% is usable by humans. This small amount of water is not evenly distributed around the world, resulting in a number of countries and regions facing high water stress.* If the earth's temperature continues to increase due to climate change in the future, the sea levels will rise owing to the thermal expansion of the oceans and melting ice caps. Such a situation could result in rivers being contaminated with salt water, a rise in groundwater levels, or other disasters with the potential to reduce the amount of fresh water available to humans. Meanwhile, United Nations World Water Development Report 2023 states that global water use volumes have risen by around 1% each year over the past 40 years, and this pace of increase is expected to continue until 2050 as a result of factors such as population growth and social and economic development. In light of this situation, companies must address the issues regarding global water resources in order to conduct sustainable business activities.
* Degree of stress in the water supply–demand balance
Water Stress Levels Around the World

Reasons for Addressing Social Issues
Mazda forecasts progress in various initiatives aimed at realizing a recycling-oriented society from the perspective of natural capital to be seen around 2030. This progress will be achieved by using resources without any losses; promoting the 3Rs to encourage the reuse of water, plastic, and other resources; and establishing circular economies and other resource circulation systems. Meanwhile, a significant reduction in energy and resource losses can be expected as a result of efforts to make processes more energy and resource efficient across the vehicle manufacturing supply chain. Dramatic progress will also likely be made in recycling and waste reduction initiatives through the promotion of the 3Rs and the transition to a circular economy. Aiming to become a company that can coexist in harmony with the earth, Mazda will continue to implement exhaustive recycling and waste reduction initiatives.