Mazda promotes safety and security initiatives from the three perspectives of vehicles, people, and roads and infrastructure to create infrastructure that allows everyone to move freely and enjoy a fulfilling life. The Company thereby aims to contribute to the realization of an automotive society that offers safety and peace of mind.
REALIZATION OF AN AUTOMOTIVE SOCIETY THAT OFFERS SAFETY AND PEACE OF MIND
- Basic Approach
- Goals
- Initiatives (Development and Commercialization of Safe Vehicles)
- Basic Safety Technologies
- Advanced Safety Technologies
- Advanced Driving Support Technology
- Third-Party Evaluations of Mazda's Safety Technologies
- Initiatives (Safety Awareness Raising)
- Initiatives (Coordination with Traffic Infrastructure)
Basic Approach
Three Perspectives of Safety and Security Initiatives
Mazda's Safety Philosophy
Mazda Proactive Safety is Mazda's safety philosophy. Mazda places this philosophy at the heart of its research on and development of safety technologies. Ensuring safe driving under a variety of circumstances requires one to operate their vehicle while predicting potential risks of accidents and making appropriate decisions. However, no matter how careful people are, some accidents cannot be avoided. To address such accidents, the Company is utilizing the insight gained through years of research on human-engineering mechanisms to develop advanced safety technologies that reduce the risk of being exposed to dangerous circumstances, as opposed to responding once a dangerous circumstance has arisen. These technologies are offered to drivers under Mazda Proactive Safety.
Mazda Proactive Safety: Mazda's Safety Philosophy


Building Block Concept for Safety Technology
In addition to refining its safety technologies, Mazda promotes technology development based on the belief that the very act of spreading these technologies throughout society is a way of demonstrating the value it offers. In developing safety technologies, the Company applies the Building Block concept in a manner similar to the approach used for environmental technologies.
Building Blocks Toward the Realization of an Automotive Society that Offers Safety and Peace of Mind


Goals
Based on an original safety concept, Mazda Proactive Safety, Mazda is continuing to develop advanced driving support technologies that utilize IT. The Company is also working to create vehicles that enhance the safety and peace of mind for drivers, passengers, and everyone else around. In terms of what Mazda can achieve through automotive technologies, the Company aims to achieve zero deaths resulting from its new vehicles by 2040.
Initiatives (Development and Commercialization of Safe Vehicles)
Basic Safety Technologies
Basic technologies are a crucial performance element underpinning the safety we feel in our everyday lives. For this reason, Mazda promotes the continuous evolution of basic safety technologies and will install these technologies in all vehicles as standard to contribute to the realization of an automotive society that offers safety and peace of mind.
Support for Assuming the Ideal Driving Position
Mazda believes that the ideal driving position not only allows drivers to properly control a vehicle but can also improve their handling when attempting to avoid emergency collisions and reduce injury to occupants should a collision occur.
Ideal Pedal Layout
Mazda offers a layout for brake and accelerator pedals located where the driver can stretch their foot forward and naturally rest it on the accelerator pedal when siting in the driver's seat in order to allow people to enjoy safe and comfortable driving with the ideal driving position. The distance between the accelerator pedal and the brake pedal has also been optimized. Allowing drivers to sit in a more natural position is anticipated to reduce driving fatigue and lower the possibility of the driver stepping on the wrong pedal when braking in an emergency. Many vehicles employ a pedal design in which pedals are suspended from the structure below the steering wheel. Mazda vehicles, meanwhile, employ an organ-type design for their pedals in which the motion of pedals when depressed mirrors the motion of the foot being used to depress them. With this design, the driver's foot and the pedal follow the same trajectory when the driver's heel is placed on the floor. This minimizes deviations in its trajectory and makes it easier to control the accelerator pedal while reducing leg fatigue on long drives.
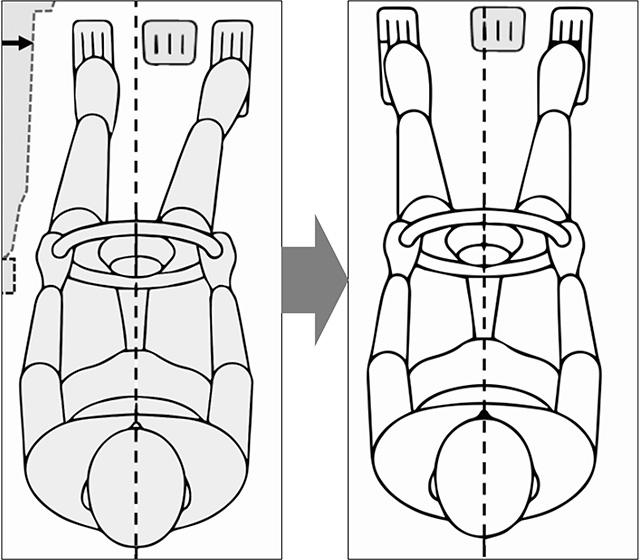

Comfortable pedal layout enabling easy operation from a natural position
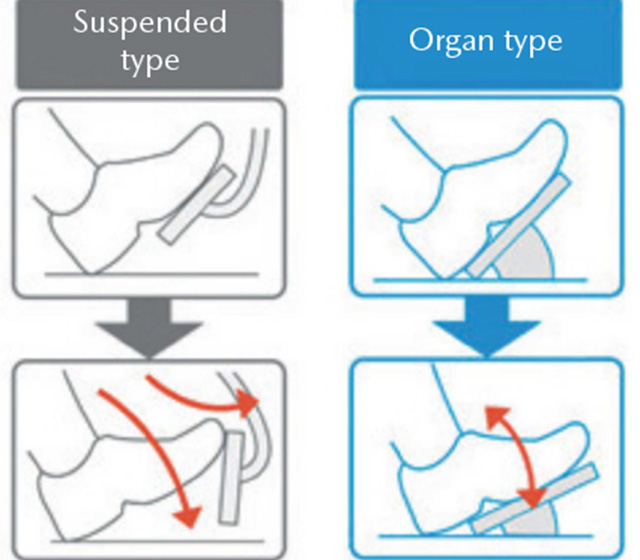

Organ-type accelerator pedal
Support Using Automatic Driving Position Guide
Large product group vehicles launched after 2022 (the CX-60, CX-70, CX-80, and CX-90) have incorporated an automatic driving position guide to help as many people as possible achieve an ideal driving position.* As one of Mazda's driver personalization systems, this feature estimates the driver's physical build based on the body data that they have input in advance as well as by detecting the positions of their eyes with a camera. This feature will then automatically adjust the positions and angles of the driver's seat, the steering wheel, the Active Driving Display (ADD), and the outer mirrors. The driver can also make fine adjustments on their own.
* The feature is only available for certain vehicle grades.
Enhanced Visibility
Mazda considers it important to secure good visibility to help the driver identify and react to their surroundings, such as road environment, other vehicles, obstacles, and pedestrians including children. Accordingly, door mirrors on all Mazda passenger vehicles currently available on the market are installed on the outer door board in a lower position to expand the scope of visibility through the mirror. For the 2019 Mazda3 and subsequent models, visibility has been further enhanced via a combination of the inherent slenderness and the well-devised shape of the A-pillar, which reduces blind spots. One of the areas where increased visibility is noticeable is during left turns, which are at high risk for coming into contact with children.
See-Through View Technology that Helps the Driver Confirm Their Surroundings
The See-Through View technology has been introduced in large product group vehicles (the CX-60, CX-70, CX-80, and CX-90) and the CX-50*1 to allow the driver to better confirm their surroundings to gain a stronger feeling of security.*2 This technology uses a camera system that has the three functions of detection, identification, and collision prediction. With this camera system, the technology complements the driver's vision by displaying an image of the surroundings as if they are seen from inside the car. This technology is useful in quickly identifying objects or pedestrians and can also help alleviate concerns when parking or starting the car.
- Detection
Integration of a front-view (or rear-view) image with part of a side-view image to broaden the field of vision - Identification
Modification of images to show objects in a larger size and three-dimensionally so that they appear as though they are being viewed diagonally (from the driver's seat) - Collision prediction
Display of the outermost side of the car and its predicted line of course
*1 This feature is equipped on 2024 models and products released thereafter.
*2 The feature is only available for certain vehicle grades.
HMI Concepts for Minimizing Causes of Careless Driving
Mazda has advanced development on human machine interfaces (HMIs), which denote equipment and mechanisms that facilitate communication of information about various inputs occurring during driving between the driver and the vehicle based on the concept of a "Heads-up Cockpit." This concept is meant to allow people to focus on driving while considering a variety of information but still prioritizing safety.
Based on Mazda's human-centered design philosophy for HMI, the cockpit is designed to minimize three risk factors for careless driving*1 (cognitive distraction, visual distraction, and manual distraction) to enable the driver to concentrate on driving. The information necessary for driving is presented in order of priority so that the driver can concentrate their attention on driving and thus reduce cognitive distraction. Indications around the driver's seat have been simplified to make the display easier to see and thus reduce visual distraction. Meanwhile, indicators and other intuitively operable devices are installed to reduce manual distraction. The CX-60 was the first model to be equipped with an HMI that featured an advanced indicator system based on an enhanced human-centered design philosophy.*2 One of the most prominent advancements of this system lies in the increased area of the ADD, which displays vehicle and navigation information. Large product group vehicles launched after the CX-60 feature an ADD that is three times larger than ADDs in preceding models. In conjunction with the enlargement of the ADD, the indicator layout has also been designed and the size of characters and graphics has been increased to make displayed information more recognizable and more quickly readable.
*1 The following are three risk factors for careless driving.
・Cognitive distraction: When the driver is distracted by something other than vehicle control, such as checking the position of a switch or its operation method
・Visual distraction: When the driver takes their eyes off the road to check information or for other purposes
・Manual distraction: When the driver makes large movements of their body and adopts an awkward posture to operate a device
*2 The feature is only available for certain vehicle grades.
Cockpit Design that Enables the Driver to Better Concentrate on Driving


- Vehicle speed and other active information that should be checked at every moment is shown in the ADD.
- The amount of fuel and other status information necessary for checking the status of the vehicle is displayed via meters.
- Media information and other information for comfort and convenience is shown in the center display.
Collision Safety Technologies
Mazda has been developing technologies for minimizing injuries to the driver, passenger, and pedestrians and damage to other vehicles in the event of an accident. Our approach has been focusing on analyzing various real cases of accidents and a variety of examples of actual accident-caused injuries and damage as well as understanding on human-engineering mechanisms that cause injuries to people's bodies gained through relevant research.
Lightweight Collision-Safe Body
Mazda has developed a sturdy vehicle body structure that can absorb energy extremely efficiently by introducing highly durable material for pillars and frames, reinforcing skeleton joints, and designing the optimal forms of skeleton joint sections. This body structure can absorb and disperse impacts in various directions to support the cabin and minimize its deformation.
Occupant Protection
Mazda has developed a technology for reducing injuries based on research on the human characteristics of people who are different in terms of build and of elderly and other groups of people. Mazda vehicles use an occupant-protection structure designed to prevent various forms of accidents and injuries.
Pedestrian Protection
As a technology for minimizing injuries to drivers, passengers, and pedestrians in the event of an accident, Mazda vehicles use a pedestrian-protection structure designed to prevent injuries in various spots in people's bodies.
Advanced Safety Technologies
i-Activsense
Mazda is committed to continuous evolution of i-Activsense* advanced safety technologies to deliver safer, more reliable vehicles to a greater number of customers, ranging from beginners to elderly drivers. We use "i-Activsense" as an umbrella term that covers all of the advanced safety technologies developed in line with Mazda Proactive Safety principles. These technologies include active safety technologies, which support safer driving by helping the driver to recognize potential hazards, as well as precrash safety technologies, which help to avert collisions when an accident may be difficult to prevent or reduce their severity in situations where they cannot be avoided.
* i-Activsense technologies are designed to help reduce damage and/or injuries resulting from accidents. However, each system has its limitations, and no safety system or combination of such systems can prevent all accidents. These systems are not a replacement for safe and attentive driving. Please drive carefully at all times and do not rely on technology to prevent an accident.
Advanced Safety Technologies i-ACTIVSENSE (in Japanese only)
Advanced Driving Support Technology
Mazda Co-Pilot Concept
Mazda has conducted extensive research on human-engineering mechanisms. By understanding and modeling physical bodies and brain mechanisms, the Company has come up with the Mazda Co-Pilot Concept, an advanced driving support technology that can help to reduce risks associated with the driver becoming sleepy or unwell. Under this concept, people can enjoy driving and feel revitalized mentally and physically while the car tracks all the movements of the driver and drives "virtually" in the background at all times. If the unexpected occurs, such as the driver suddenly losing consciousness, the car takes control to help prevent an accident and reduce potential injuries. It also automatically contacts emergency services and drives to a safer location to protect bystanders and the surrounding areas. The Company aims to develop technologies of the Mazda Co-Pilot Concept, which uses autonomous driving technologies to allow drivers to enjoy any drive with peace of mind, and make these technologies standard.
Driver Monitoring
Mazda's Driver Monitoring system, which was first introduced in the Mazda3 in 2019, features two functions: step-by-step warnings issued when the driver's drowsiness is detected and an earlier frontal collision warning issued when careless driving is detected. More advanced technologies were applied to the CX-60 beginning in 2022 to detect drowsy driving with the driver's eyes closed and identify sudden changes in the driver's condition based on changes in their posture or the position of their head in addition to issuing warnings against careless driving. The accuracy of the Driver Monitoring system's detection of both drowsiness and changes in the driver's condition has been increased through comprehensive judgment based on various factors, including driving inputs.


Detection of Driver Condition Through Driver Monitoring System


Driver Emergency Assist System
Starting with the CX-60, Mazda has been equipping its vehicles with the Driver Emergency Assist (DEA) system,* an advanced safety technology that can detect abnormalities in the driver's condition to help avoid an accident or reduce damage and injuries. Through linkage with the Driver Monitoring system, the DEA system will slow down and stop a vehicle if it becomes difficult for the driver to continue to drive due to a sudden sickness or for other reasons, regardless of whether the vehicle is running on an expressway, a road designated only for automobile usage, or a regular road. This system therefore helps avoid accidents or minimize accident damage and injuries. In April 2023, the system was recognized with an Ichimura Industrial Achievement Award at the 55th Ichimura Industrial Awards (organized by the Ichimura Foundation for New Technology).
【Related Article (MAZDA MIRAI BASE)】
Driver Emergency Assist in Mazda's CX-80: Program manager's Vision for a Trusted Co-Pilot
* The features of the DEA system vary by vehicle grade. The DEA system will slow or stop a vehicle in an attempt to avoid an accident or minimize its damages. This system will function only under certain conditions and will not function if these conditions are not met. Moreover, these features have limitations and their effectiveness may vary due to a variety of conditions. Even if the system functions as intended, it does not guarantee that a collision or departure from the road will be completely avoided. It is the responsibility of the driver to drive safety and the driver bares full responsibility for the functioning of the DEA system. Please drive carefully at all times and do not rely on technology to prevent an accident. For details, please ask dealer staff or refer to Mazda's website.
Third-Party Evaluations of Mazda's Safety Technologies
(April 1, 2024–March 31, 2025)
| Country/Region | Third-Party Evaluation Program | Rating | Vehicle Models | Ratio of Vehicles Receiving Said Rating to Total Vehicles Rated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | JNCAP*1 | 5 stars (highest rank) | CX-80 | 1/1 |
| United States | USNCAP*2 | 5 stars (highest rank) | MAZDA3, CX-30, CX-5, CX-50, and CX-90 | 5/5 |
| IIHS*3 | Top Safety Pick+ | MAZDA3, CX-30, CX-50, CX-70, and CX-90 | 5/5 | |
| Europe | Euro NCAP*4 | 5 stars (highest rank) | CX-80 | 1/1 |
| Australia / New Zealand | ANCAP*5 | 5 stars (highest rank) | CX-80 | 1/1 |
For more information on past and latest ratings by country or region, please refer to the Safety page of Mazda's corporate website.
*1 The Japan New Car Assessment Program is a safety rating program introduced by the National Agency for Automotive Safety and Victims' Aid in 1995 to encourage the proliferation of safe vehicles. Vehicles are rated based on their preventative safety and collision safety performance as well as their automated accident reporting systems.
*2 The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration's 5-Star Safety Ratings program rates overall safety performance with 5 stars being the highest possible rating.
*3 In the overall safety rating program of the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety, Top Safety Pick+ is the highest possible rating.
*4 The European New Car Assessment Programme is administered by an independent agency comprised of the transport authorities of European countries. In this program, 5 stars is the highest possible rating.
*5 The Australasian New Car Assessment Program is an overall safety rating program operated by municipal government agencies in Australia and New Zealand. In this program, 5 stars is the highest possible rating.
Initiatives (Safety Awareness Raising)
It is said that most traffic accidents are caused directly or indirectly by human behavior. Mazda endeavors to raise safety awareness among adults and children through various means of communication.
Traffic Safety Awareness Raising
In cooperation with local municipalities and organizations, Mazda conducts various activities to raise safety awareness with the goal of decreasing causalities from traffic accidents. For example, the Company has been partnering with the Hiroshima Branch of the Japan Automobile Association (JAF) since 2017 to communicate the importance of seatbelt use by everyone in a vehicle. This importance is illustrated through the simulation of a collision at a speed of five km/h using Seat Belt Convincers, quizzes to raise children's safety awareness, and shock absorption experiments with toy cars. We are also partnering with Hiroshima City to provide accurate information to pregnant individuals and their families in order to protect pregnant individuals and unborn babies from traffic accidents. As one facet of these activities, Mazda is coordinating with municipal government agencies and obstetricians in Hiroshima Prefecture and distributing original informative fliers, displaying safety posters, and supplying video content.
【Statistics from FY March 2025】
- Participation in the Traffic Safety Challenge Festa held at Numaji Transportation Museum (Hiroshima City's traffic science museum) and at 5-Days Children's Museum
- Organization of traffic safety quizzes, shock absorption experiments with toy cars, and other safety awareness-raising activities during weekend openings of the Mazda Museum
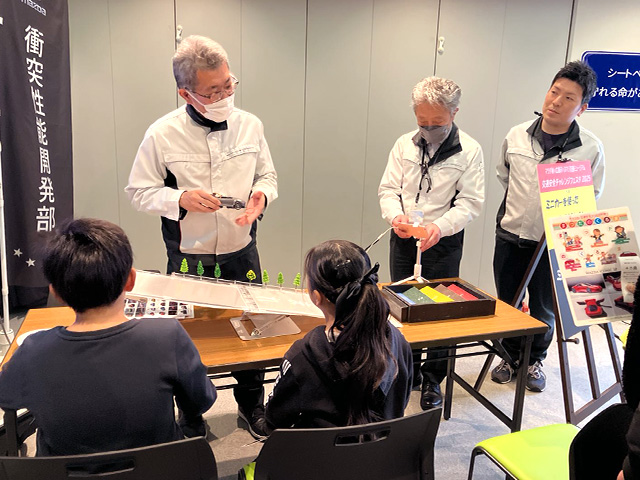




Seatbelt and child seat use awareness-raising activities
Safe Driving Demonstrations
Mazda has been holding Mazda Driving Academy programs since FY March 2015. Through this program, we aim to help customers in Japan learn the theories and techniques for driving their cars easily, comfortably, and safely.
【Statistics from FY March 2025】
- Mazda Driving Academy held nine times
For more information, please refer to MAZDA OFFICIAL WEBSITE (in Japanese only)
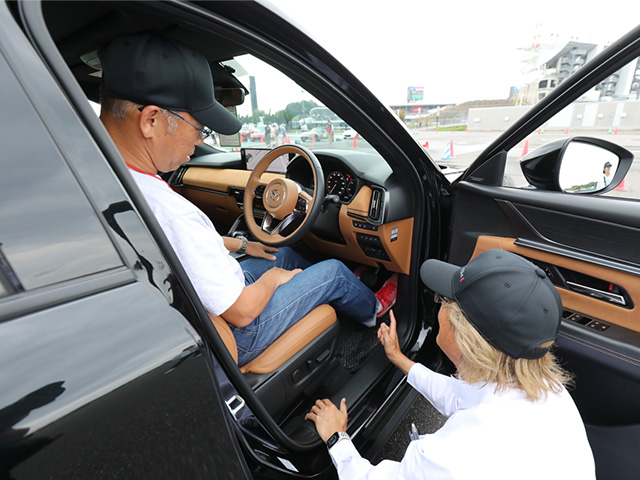


Driving position instruction
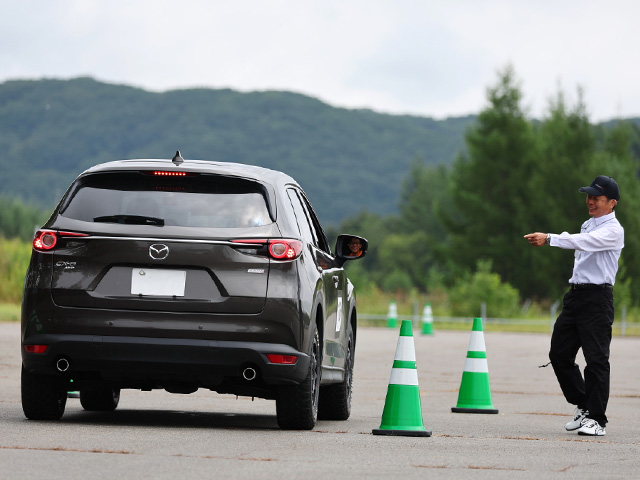


Sudden braking experience
Safe Driving Instruction for Elderly Drivers
Together with Miyoshi City in Hiroshima Prefecture, Mazda helped launch the Miyoshi Iki-Iki Safe Drive Campaign, a program for supporting elderly drivers in continuing to drive safely, in September 2024. This campaign is one of the initiatives of the safe driving support for the elderly subcommittee of the Tateshina Meeting. As part of this campaign, telematics tags, which record driving behavior, were attached to the personal vehicles of roughly 300 elderly drivers living in Miyoshi City to collect driving data. Moreover, a smartphone app was used to provide these drivers with information on sudden braking and excessive acceleration during their driving for use in improving their personal driving habits. This information was also used to prepare a traffic safety map detailing areas of the community that are dangerous from a traffic perspective, such as points prone to sudden braking. This map was then presented to Miyoshi City in February 2025.
【Related Article (News Release)】
Mazda Presents Traffic Safety Map to Miyoshi City as Part of Initiative Under Safe Driving Support for the Elderly Subcommittee of the Tateshina Meeting (in Japanese only)

Initiatives (Coordination with Traffic Infrastructure)
Intelligent Transport System Initiatives for Realizing a Safe Automotive Society
Traffic accidents and congestion are serious social problems in many countries and regions. To address these problems, worldwide efforts have been taken to introduce advanced technologies for roads and automobiles. As an automobile manufacturer, Mazda has been proactively supporting the intelligent transport system project* driven by the government and private sector, and is working collaboratively with national and local government agencies and relevant companies in order to realize a society where the road traffic is safe and accident-free.
* Intelligent transport systems use telecommunications technology to connect vehicles, people, and the traffic infrastructure with the aim of easing traffic congestion and reducing the number of accidents throughout Japan.
Technology for Notifying Drivers of Unseen Dangers
Mazda is promoting research and development of intelligent transport systems as a means of monitoring objects too far from vehicles to be detected by Mazda's i-Activsense advanced safety technology or the areas of intersections that cannot be seen by the driver.
Intelligent Transport System Projects in Which Mazda Participates
| Project | Description | Organizer |
|---|---|---|
| ASV (Advanced Safety Vehicle) Project |
This project entails research and development to create a system for assisting safer driving utilizing cutting-edge technologies, including communication-based driving safety support systems. In 1991, the project's first phase was launched, and currently discussions are underway as to the seventh phase. | Road Transport Bureau, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism |
| Automated Driving Service Support Project | This project is promoting data utilization through coordination between the various activities of government agencies and private-sector companies, such as the development of safety information distribution systems that link vehicle probes, weather forecasts, and other information sources. | Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry |