Mazda respects the principles of Japan's Corporate Governance Code, formulated by Tokyo Stock Exchange, Inc., and works to maintain strong relationships with its stakeholders, including shareholders, customers, suppliers, local communities, and its employees. By doing so, the Company strives to sustain growth and enhance its corporate value over the medium and long term through transparent, fair, prompt, and decisive decision-making and to continue to enhance its corporate governance.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Basic Approach
Relevant Documents
Frameworks
Corporate Governance Framework
The Company's business environment is undergoing rapid changes. In order to enable faster business decision-making, further enhance discussion of management strategies, and strengthen supervisory functions of the Board of Directors, the Company has adopted the company with audit and supervisory committee structure described in the Companies Act of Japan. Based on this structure, the Company maintains legally mandated governance organizations including the general meeting of shareholders, the Board of Directors, and the Audit & Supervisory Committee. Furthermore, to raise the transparency of the processes behind the nomination and selection of officers and the remuneration decision-making process, the Company established the Officer Lineup & Remuneration Advisory Committee as an advisory body to the Board of Directors.
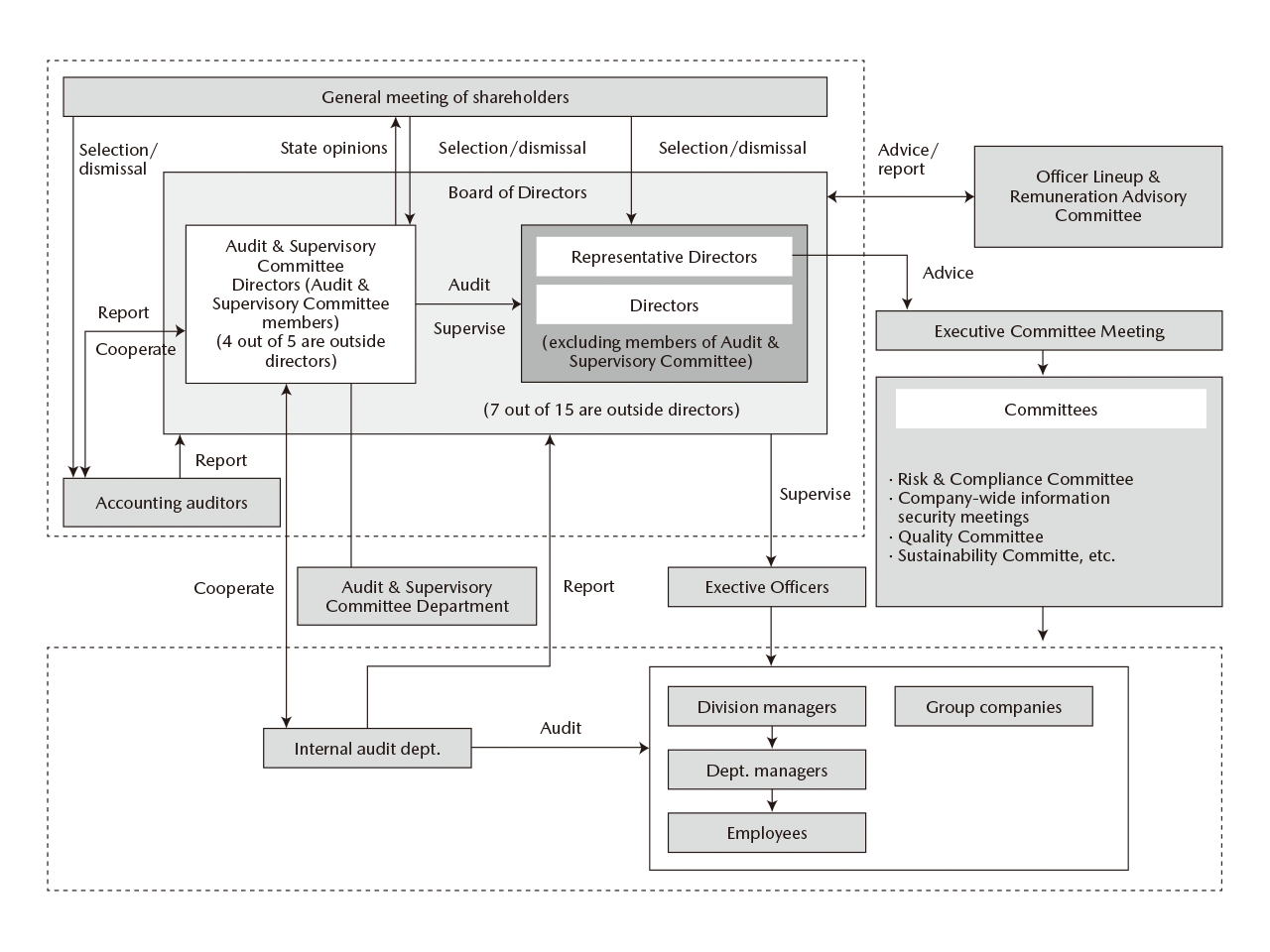

Board of Directors
The Company's board of directors deliberates and makes decisions on items related to the execution of important business, such as management strategy and basic management policies, and supervises the execution of individual directors' duties. In addition, facilitate quick and flexible decision-making, based on the Articles of Incorporation a substantial part of decision-making regarding the execution of important business will be delegated to management, and executive directors including and below the president to whom authority has been delegated based on the Company's rules of administrative authority will make decisions regarding these matters. The board is made up of 15 directors, seven of whom are highly independent outside directors. The board of directors generally meets once per month.
【Major Matters Discussed in FY March 2025】
- Electrification and market strategy for 2030.
- Progress of measures for achieving management that is conscious of cost of capital and stock price.
- Approach to issues around sustainability and progress of action for human rights due diligence.
- Status of operation of systems for internal control and risk management. (efforts to prevent the recurrence of inappropriate incidents in Applications for Type Designation, measures to cybersecurity risks, and others.)
Audit & Supervisory Committee
The Company's Audit & Supervisory Committee audits and supervises the board of directors' decision-making process and business execution through the execution of voting rights at board of directors meetings and the execution of its right to state opinions on the personnel changes and remuneration of directors (excluding directors who are Audit & Supervisory Committee Members) at the General Meeting of Shareholders. The Audit & Supervisory Committee is made up of five members, four of whom are highly independent outside directors. To ensure the smooth operation of the Audit & Supervisory Committee's audits, one of its members is full-time.
【Major Matters Discussed in FY March 2025】
- Audit policy, high-priority initiatives, audit plan, work assignment, audit methods for effective functioning of audit activities.
- Strengthening the mechanisms and means to reflect the opinions of outside directors based on multifaceted perspectives and outside viewpoints in audits while striving to enhance the opportunities to provide outside directors with information, as well as the nature of such information.
- Checking and enhancing the execution of duties (including the formulation and progress of management strategy matters) by directors (excluding directors who are Audit & Supervisory Committee members), executive officers, general managers of major departments, and management of subsidiaries and affiliates.
- The cooperation with the Internal Audit Department and accounting auditor as an organizational audit.
- Evaluating appropriateness of audit by the accounting auditor based on quarterly reviews and reports by the accounting auditor, evaluating validity of the selection and dismissal of the accounting auditor and remuneration for the accounting auditor.
Accounting Auditors
Accounting audits are conducted by KPMG AZSA LLC. The certified public accountants who conducted the Company's accounting audits are Hiroshi Tawara, Koji Yoshida, and Kazumi Kanehara. Those assisting with the Company's accounting audits include 16 certified public accountants and 36 others, four of whom have passed the certified public accountant examination.
Executive Officers
Mazda has introduced an executive officer system. By separating the execution and management functions, Mazda seeks to enhance the effectiveness of the Board of Directors as an oversight organization. In addition, decision-making is expedited through expanded discussion by the Board of Directors and by delegating authority to executive officers. In this way, the Company is working to further managerial efficiency.
Officer Lineup & Remuneration Advisory Committee
The Company established the Officer Lineup & Remuneration Advisory Committee, made up of three representative directors and seven outside directors and chaired by a representative director, as an advisory body to the board of directors. The committee reports to the board of directors the results of its deliberation on matters such as officer lineup and policies regarding the selection and training of directors, as well as remuneration payment policies and the remuneration system and process based on those policies, which contribute to the Company's sustainable growth and raising of corporate value in the medium and long term.
【Major Matters Discussed in FY March 2025】
- Appropriateness of the composition of directors and executive officers to ensure the diversity and skills mix required to achieve management policy goals (executive personnel changes effective April 1 and June 25, 2025)
- Appropriateness of remuneration amount for directors and executive officers (ensuring conformity with the policies on determining details of individual remuneration levels for directors (excluding directors who are Audit & Supervisory Committee members) and comparison with the remuneration levels of the benchmark companies whose size and line of business are similar to those of the Company, etc.)
- Appropriateness of standard amounts, performance indicators, and target values, etc. of the restricted stock remuneration and the performance share unit remuneration.
Cooperation among Parties Responsible for Auditing
The Audit & Supervisory Committee regularly meets with the accounting auditors and hears explanations of their audit plans, audit issues, and results. The Audit & Supervisory Committee also provides necessary information on its audit plans and the status and result of audits. In this way, information is exchanged in both directions and the Company is working to strengthen this close cooperation. Also, some audits, such as physical inspections of inventories and securities, are conducted jointly by the Audit & Supervisory Committee and the accounting auditors. In addition, the Audit & Supervisory Committee regularly holds meetings with the group of the accounting auditors and internal audit department and with the group of the internal audit department and the departments in charge of promoting internal and financial control. The Audit & Supervisory Committee receives reports from the internal audit department on the plans for and results of internal audits of the Company and the Group companies. It also receives reports from the departments in charge of promoting internal and financial control on plans for efforts to enhance internal and financial control in the Company and the Group companies and the status of these efforts. In addition, the Audit & Supervisory Committee provides information acquired in the process of conducting its audits or conveys requests from its perspective as the Audit & Supervisory Committee, making for two-way exchange of information.
Board of Directors
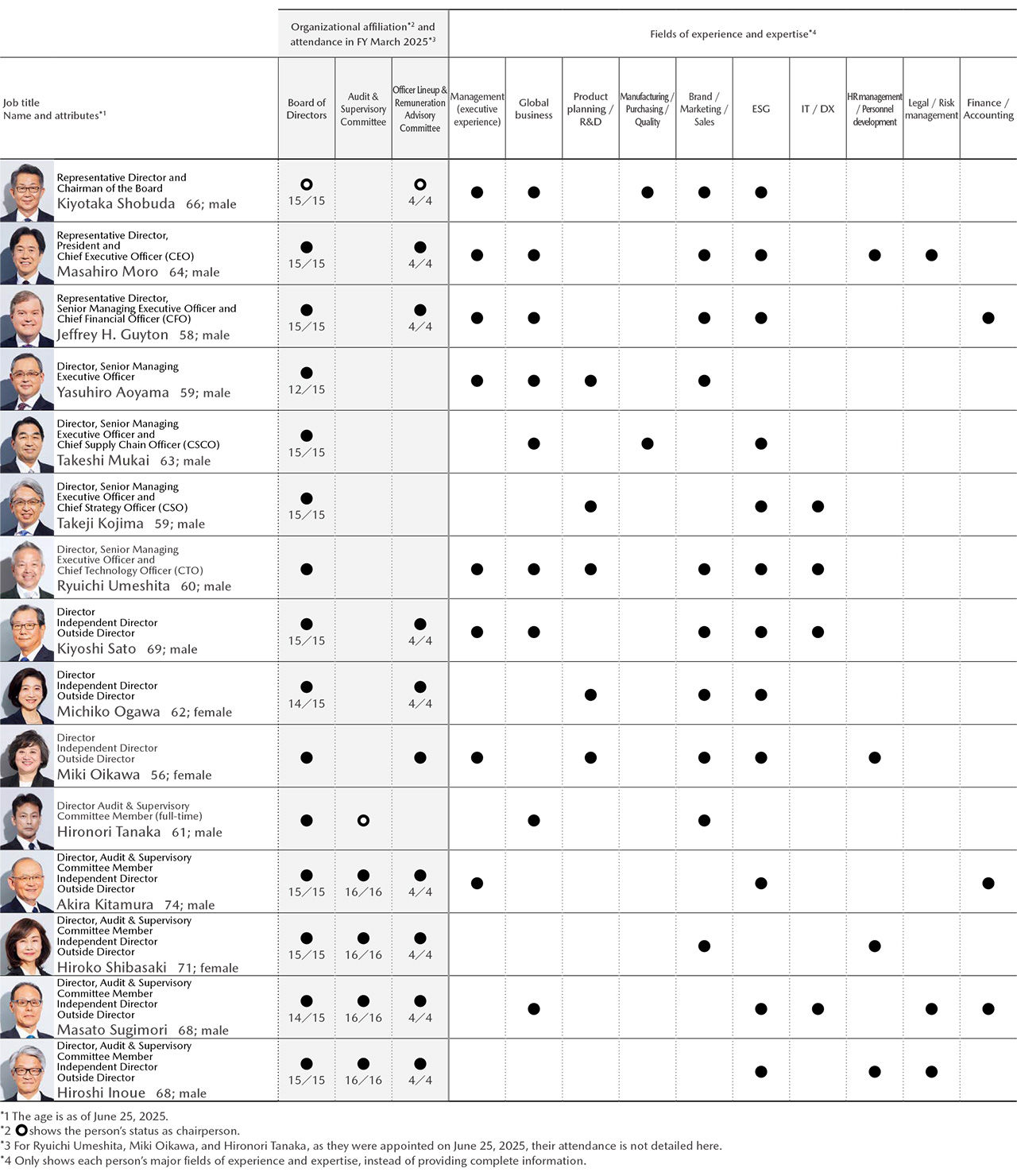
Skills Matrix of the Board of Directors
As the business environment surrounding the Company rapidly changes, Mazda believes that the Board of Directors must have an appropriate balance in knowledge, experience, and competence and also be diverse in composition to effectively fulfill its roles and responsibilities for the Company’s sustainable growth and the raising of corporate value in the medium and long term.
Organizational Affiliation (As of June 26, 2025)
Board of Directors (including members of Audit & Supervisory Committee) |
Number | 15 (Inside directors: 8, outside directors: 7), including 3 female directors and 1 foreign-national director |
|---|---|---|
| Ratio of Outside Directors | 46.7% | |
| Ratio of Female Directors | 20.0% | |
| Audit & Supervisory Committee | Number | 5 (Inside directors: 1, Outside directors: 4), including 1 female director |
Officer Lineup & Remuneration Advisory Committee |
Number | 10 (Inside directors: 3, Outside directors: 7), including 3 female directors and 1 foreign-national director |
| Ratio of Outside Directors | 70.0% |

Outside Directors
Mazda selects outside directors with independent standpoints to strengthen the oversight function of the Board of Directors and improve the transparency of management. Outside directors are judged to be sufficiently independent when they meet the Company’s criteria for determining the independence of outside officers.
Criteria for Determining the Independence of Outside Officers and Reasons for Appointment
Support System for Outside Directors
The company provides explanations of matters to be brought before the Board of Directors as necessary so that outside directors can freely state their opinions at Board meetings and so that outside directors can easily participate in decision-making. The Company also arranges for outside officers to interview executive officers and provides opportunities for them to inspect facilities and participate in events both inside and outside the Company.
Audit & Supervisory Committee members (full-time) offer observations based on information they have acquired or opinions they have formed through their attendance at important internal meetings or through their audit activities. The departments concerned work together to provide information based on the opinions of the outside directors and to support them.
Analysis and Evaluation of the Board's Effectiveness
To assess the current effectiveness of the board of directors and to steadily promote measures for further improvement, the Company conducts an annual analysis and evaluation of the effectiveness of the board of directors.
【The method of analysis and evaluation and an overview of the results of the evaluation for effectiveness in FY March 2025】
(1) Method of analysis and evaluation
- Survey method: questionnaire (4-point rating scale and free comments)
- Areas evaluated: Structure of the board, Matters to be deliberated on / timing / duration, Materials and briefings, Support for outside directors, Status of deliberations, Monitoring and internal control and Other.
Evaluation process:
① All directors complete a survey (self-evaluation)
② Survey results are compiled and summarized
③ A discussion is held to identify areas to be reviewed and propose effective improvement measures based on the survey results
④ The board of directions on improvement measures
(2) Overview of results
General comments
The board of directors confirmed that 1) all directors are appropriately involved in decision-making on important matters concerning the Company's management, 2) outside directors express their opinions from an independent perspective after gaining an understanding of the Company's situation through briefings on proposals beforehand and other forms of support, and 3) oversight of the execution of operations is ensured.
Furthermore, the board of directors confirmed that delegation of its authority to representative directors within the appropriate scope under the Company's Articles of Incorporation has expedited decision-making, and that securing ample time for deliberation has resulted in more productive discussions.
Areas to be reviewed and measures
Status of measures taken in previous implementation (effectiveness in FY March 2024)
Areas identified in points for consider in previous implementation Summary of measures taken Further deepen discussion of medium- to long-term strategies - Amid significant changes in the business environment of each market due to electrification, the board of directors discussed marketing strategies based on reports presented at BOD meetings.
- The board of directors held an off-site meeting to align their views and exchange opinions with outside directors regarding management issues as well as strategies and their progress.
Hold ongoing discussions on key themes that need reinforcing - The board of directors shared their views and came to an understanding of key themes that need reinforcing (such as sales strategy, sustainability, and cybersecurity), and discussed these key themes based on reports presented at BOD meetings.
Implement measures to further improve the quality of discussions - The board of directors discussed and came to an agreement regarding the preparation of materials that clearly and concisely summarize the key points of discussions.
- The board of directors regularly conducted prior briefings for outside directors on proposals and shared other information with them.
Areas identified in FY March 2025 and future measures
As a result of this year's evaluation, the board of directors confirmed that while there have been improvements in areas identified points for consider in the previous implementation, further reinforcement of these improvements through the following measures is necessary.
Areas identified points for consider in this implementation Summary of measures taken Further deepen discussion of medium- to long-term strategies - In addition to the presentation of and regular reporting on market and product strategies to the board of directors, the board of directors will utilize off-site meetings and other opportunities to engage in more planned and detailed exchanges of opinions with outside directors regarding management issues, strategies, and their progress.
Hold ongoing discussions on key themes that need reinforcing - Based on content reported in FY2024, the board of directors will discuss and come to an agreement on how to report on key themes and will incorporate this into the annual plan to be submitted.
Implement measures to further improve the quality of discussions - The board of directors will ensure the use of materials that clearly and concisely state the key points of discussions, and the provision of comprehensive briefings that emphasize the main points.
- The board of directors will ensure all directors have a common understanding on how to report on the status of the execution of duties and other matters.
- The board of directors will ensure outside directors are given prior briefings on proposals and other information is shared with them.
Executive Remuneration
In June 2024, a revision was instituted to the remuneration systems for directors (excluding directors who are Audit & Supervisory Committee members and outside directors), executive officers, and fellows. This revision was designed to heighten motivation for pursuing medium- to long-term improvements in corporate value by increasing the degree to which officers share the benefits and risks of share price fluctuations with shareholders. Remuneration is comprised of basic remuneration, performance-based monetary remuneration, and restricted stock remuneration.* The ratios of these different forms of remuneration are set to be around the levels described below when all of the targets of the medium-term management plan and the targets for all of the performance indicators defined for performance share units are accomplished. Directors who are Audit & Supervisory Committee members and outside directors receive a fixed amount of basic remuneration only, considering their independence from the execution of operations.
* Restricted stock remuneration is comprised of restricted stock that is not linked to performance and performance share units that are linked to performance.
Structure of remuneration for directors


| Remuneration category | Details | Performance indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Basic remuneration | Fixed-sum payments based on the director’s position and responsibilities | ― |
| Performance-based monetary remuneration | Payments based on the director's position and responsibilities that are adjusted in accordance with the degree of progress toward the initially announced performance forecasts for defined performance indicators. Also, payments based on personal evaluations that reflect the degree of accomplishment of targets set for each individual. | ■Consolidated net sales ■Net income attributable to owners of the parent |
| Restricted stock compensation | Number of shares issued based on standard value set in accordance with the director’s position and responsibilities | ― |
| Performance-based performance share units | Number of units allocated equivalent to the base amount (1 unit = 1 share equivalent) based on the director’s position and responsibilities and used to determine the number of shares to be issued based on whether the target for each performance indicator was achieved after the performance evaluation period (one fiscal year in which the unit grant date falls) | ■Return on equity ■Employee engagement* ■Customer focus enhancement* ■Greenhouse gas emission reduction |
* Employee engagement and customer focus enhancement are measured based on rates of positive responses in regard to relevant questions on Global Employee Surveys.
Executive remuneration amounts in FY March 2025
Annual Securities Report for FY March 2025 Corporate Governance(P78)
Cross-Shareholdings
(1) Policy on cross-shareholdings
Taking into overall consideration the business strategy, the necessity of business activities such as maintaining and strengthening business dealings, and the comparison of benefits and risks of cross-shareholding with the cost of capital, the Company will have cross-shareholdings when it will lead to the raising of corporate value over the medium and long term. If the purpose of cross-shareholdings is judged to have diminished, the Company will aim to reduce cross-shareholdings, including the selling of shares based on the relevant company’s circumstances, etc.
(2) Verification by the Board of Directors
Every year at a board of directors meeting, the Company will individually verify the appropriateness of its cross-shareholdings according to the above policy.
Stocks held as of the end of March 2024 were verified at a board of directors meeting, and the rationality of those holdings was confirmed.
(3) Basic policy on exercise of voting rights
When exercising its right to vote for cross-shareholdings, the Company will comprehensively evaluate whether or not matters that have come up for a vote will contribute to enhancing the corporate value, etc., of the Company and companies in which the Company holds shares over the medium and long term; the Company will then decide whether to vote for or against any proposals.
Group Governance
Mazda has established the Group Company Management Regulations to facilitate the development and ongoing and stable growth of the entire Group and to promote appropriate governance. These regulations have been deployed to all Group companies. Mazda Group companies have established corporate governance frameworks and are pursuing enhanced cooperation between the Company and Group companies in accordance with the regulations as well as with the laws and regulations of the relevant countries and regions.
Domestic Group Companies
Domestic Group companies appoint corporate auditors to audit the execution of duties by management. In addition, Audit & Supervisory Committee Members' Meetings are arranged, which are attended by the Company's Audit & Supervisory Committee members and full-time auditors from large Group companies (as defined by the Companies Act of Japan). Furthermore, staff from Mazda's internal audit department concurrently serve as auditors of Group companies. This step is taken to reinforce governance frameworks at Group companies and to enhance coordination between the Company and Group companies.
Overseas Group Companies
Many overseas Group companies organize audit committee meetings with participation by officers and representatives from internal audit and other relevant divisions at the Company and at the respective Group companies. These audit committees are assembled on an independent basis by Group companies to gather information and share opinions on internal controls in order to guide the enhancement of internal controls at Group companies. For overseas Group companies that do not have such committees, the Company will provide guidance and support as necessary to help them improve their internal control-related initiatives.
Internal Audits
Groupwide Internal Auditing Frameworks
Coordination is pursued with the internal audit departments of Group companies to perform internal audits for the purpose of ensuring sound and efficient management. To guide internal audits, the Mazda Group Basic Internal Audit Regulations have been implemented. These regulations define basic shared provisions pertaining to internal audits, such as their role, mission, organizational position, and scope. In accordance with the regulations, the internal audit department of Mazda Motor Corporation organizes regular meetings with and training sessions for the internal audit departments of Group companies in Japan and overseas. In addition, the department also conducts various tasks, such as approval of the internal audit plans of Group companies, receipt of their internal audit reports, and follow-up monitoring of improvement activities, to ensure the consistency of auditing policies across the Group and gather audit-related information. The Company's internal audit department also evaluates the functions of the auditing departments of Group companies and offers support for their activities with the aim of strengthening the internal audit departments of the respective Group companies. The internal audit department of the Company is staffed with individuals holding Certified Internal Auditor (CIA), Certified Information System Auditor (CISA), and other qualifications. Members of the department are constantly encouraged to acquire specialized qualifications and participate in outside training programs and internal workshops in order to improve their auditing skills.
Internal Auditing Frameworks at Group Companies
At Group companies that possess their own internal audit departments, internal audits are conducted independently by these departments or through collaboration with the internal audit department of Mazda Motor Corporation. For other Group companies that do not have their own internal audit departments, audits are performed by the internal audit department of the Company. Moreover, the Company's internal audit department provides Group companies with advice regarding annual audit plans and based on the results of audits, audit-related information, and other forms of support, in order to ensure the quality of audits performed by the internal audit departments of Group companies.
System Auditing
The internal audit department of Mazda Motor Corporation and the internal audit departments of overseas Group companies conduct audits of overall IT controls concerning financial reporting and IT security for individual processes and systems with the aim of reducing IT-related risks.
Internal Controls
Mazda has established the Mazda Corporate Ethics Code of Conduct, which states action guidelines for employees, and other guidelines on financial controls and other matters. In addition, the Audit & Supervisory Committee audits the status of implementation of internal control systems. Based on these guidelines and the results of audits, departments develop rules, procedures, manuals, and other provisions to guide the establishment of internal controls. Moreover, relevant Mazda divisions provide support for internal control training and framework development in accordance with the Group Company Management Regulations to promote Groupwide coordination in the implementation of internal controls.
Mazda's Internal Controls


Internal Control Self-Diagnoses
In 1998, Mazda began conducting internal control self-diagnoses of internal controls for the purpose of spreading awareness concerning internal controls. Currently, self-diagnoses are carried out at almost all domestic and overseas Mazda Group companies. In these diagnoses, the supervisors and individuals actually in charge of developing and implementing processes and frameworks, as opposed to internal audit departments, auditing firms, or other third parties, are responsible for evaluating internal controls using a defined checklist. Through this system, departments and Group companies are able to identify inadequacies in internal controls and take actions to improve them. Moreover, the checklists are confirmed by relevant Mazda divisions and revised as necessary, and newly confirmed lists are used to update existing checklists to ensure that diagnoses are always effective and appropriate.
Internal Control Signoff System
In FY March 2007, Mazda introduced a signoff system in which the senior managers of Company departments and Group companies "sign off" on internal controls after confirming the status and issues of its organization's internal controls through auditing and self-diagnosis. In addition, a quarterly reporting system was implemented in FY March 2010 whereby quarterly reports are issued to Mazda's internal audit department to facilitate the early discovery of inadequacies. For each inadequacy reported, the deadline and responsible person for improvement are specified to facilitate speedy improvement.