Mazda is committed to managing chemical substances across all stages of vehicle life cycles, spanning from production to disposal, and to reducing exhaust emissions and fuel consumption from driving. We thereby seek to comply with all relevant regulations while ensuring that we can continue to coexist with a bountiful, beautiful earth into the future.
PREVENTION OF POLLUTION
Basic Approach
Initiatives
Cleaner Emissions
Cleaner Gas Emissions
Mazda is committed to mitigating air pollution from exhaust gas. To this end, the Company is actively developing low-emissions vehicles and launching vehicles that comply with the emissions regulations of the respective countries and regions.
Emissions Reduction Technologies
Mazda pays attention to global movements toward tighter control of exhaust emissions and fuel economy, market expansion due to rapidly growing emerging countries, and depletion of scarce resources. The Company has developed its unique high-performance, three-way catalytic converters and soot (particulate matter) oxidation catalysts, which it uses to reduce the use of precious metals and help to clean exhaust gases.
Latest Emissions Reduction Technologies
Gasoline engines
Mazda uses a system based on a three-way catalytic converter to clean emissions from both its conventional 2.5-liter straight-4-cylinder engines and its 3.3-liter straight-6-cylinder gasoline turbo engines. Combined with improved fuel control technologies that increase the speed at which the catalyst activates after starting or restarting the engine, this system enables Mazda to clear the strict emissions regulations of different countries and regions, including the super-ultra-low-emission vehicle 30 (SULEV30) regulations of the United States.
Diesel engines
To clean emissions from its 3.3-liter straight-6-cylinder diesel turbo engines, Mazda uses a system based on oxidation catalysts that also utilizes ceramic filters able to catch, collect, and clean soot. Making use of a proprietary distribution-controlled partially premixed compression ignition (DCPCI) technology developed in pursuit of ideal combustion conditions, as well as larger displacement, this simple and affordable system does not require a nitrogen oxide (NOx) purification catalyst to achieve clean emissions that easily clear Japan's Real Driving Emission (RDE) regulations.
Proper Management of Chemical Substances
Management Standards for Environmentally Hazardous Materials
Mazda has prepared its Management Standards for Environmentally Hazardous Materials for management of chemical substances facing restrictions to use across the supply chain (whether those restrictions be in the form of bans or reporting requirements) based on the relevant domestic and overseas laws and regulations.
Collection and Management of Chemical Substance Information
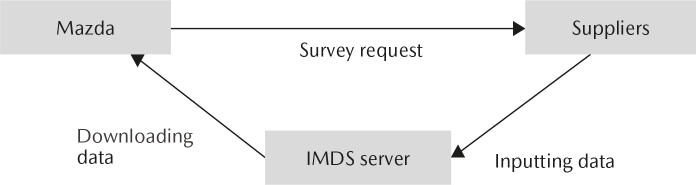
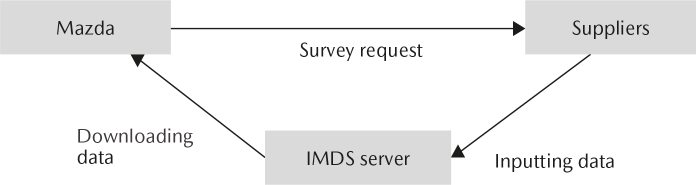
Mazda utilizes a global-standard International Material Data System to collect information on the chemical substances contained in its products. This information is used to facilitate the appropriate management of environmentally hazardous materials, such as lead, mercury, hexavalent chromium, and cadmium, across the entire supply chain.
International Material Data System-Related Measures
- The Company has developed and published a guideline that helps suppliers to correctly utilize the international material data system to communicate information.
- The chemical substance information gathered through the international material data system is used to calculate the Company's vehicle recycling rate and to comply with various regulatory regimes for chemical materials, such as Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) in Europe.
International Material Data System Framework
VOC Reduction
Reduction of VOCs in Vehicle Cabins
To maintain a comfortable cabin environment, Mazda is committed to reducing the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as formaldehyde, toluene, and xylene, which have been implicated as possible causes of sick building syndrome. In new models, starting with the Demio launched in 2007 (named the Mazda2 overseas at time of launch in 2007), Mazda is reducing VOCs in the main materials used in the cabin, such as plastics, paints, and adhesives, thereby conforming with the indoor aerial concentration guidelines established by Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
Reduction of VOCs in Painting Processes
Mazda has developed and subsequently introduced low-VOC paints for use with the Three Layer Wet Paint System, the standard process at major plants in Japan and overseas, and with the Aqua-Tech Paint System that delivers world-leading environmental performance. We have also implemented measures to achieve improved efficiency in thinner recovery for cleaning.
【Statistics from FY March 2025】
・Reduction of VOC emissions from vehicle body paint in body-painting lines to 13.0 g/m2
Adoption of Eco-Friendly Fuels
Mazda is continuing efforts to reduce the emission of sulfur oxides (SOx), NOx, dust and soot, fine particles, vapors, and VOCs. In addition, the Company is shifting from the use of fuel oil to the use of city gas for fuel and making other efforts to actively adopt materials that reduce its environmental impacts.
Reduction of Emissions of PRTR-Listed Substances
Mazda is constantly working to reduce emissions of substances listed in Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR) legislation*as it moves forward with initiatives such as the introduction of the Aqua-Tech Paint System into the painting process and improvements to the efficiency of paining processes and of thinner recovery for cleaning.
【Statistics from FY March 2025】
・Reduction of 489 tons in emissions of substances that are designated under PRTR legislation into water systems and the atmosphere (reduction of 82% from FY March 1999)
* Act on Confirmation, etc. of Release Amounts of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements to the Management Thereof