OUR COMMITMENT TO CUSTOMERS ON LEGAL COMPLIANCE


As an automobile manufacturer, I believe that it is necessary to establish and strengthen internal controls related to certification operations ourselves.
Society has a strict view of inappropriate corporate behavior, and it is obvious that behavior deviating from society's common sense and sound practices is severely condemned. We will make strict compliance with laws and regulations a top priority in all our business activities, and in addition to this, we must be strongly aware of conducting ethical and fair business operations in accordance with common sense and sound practices in society and strive to gain the trust of society.
Regrettably, in the past, we could not say that management fully understood or addressed the increased burden on certification operations in the company due to advancements in automobile technology. These advancements have led to new or updated vehicle regulatory and certification requirements, making existing processes inadequate to meet those requirements.
In response, we reviewed the certification process, schedule, man-hours, equipment, and training, and assigned a chief certification auditor (Program Manager auditing certification operation) to internal auditing division. In addition, through culture reform initiatives, we focus on fostering a corporate culture in which the operational employees play a leading role and management becomes their supporter. By doing so, we strengthen governance so that employees can work without worries, that management can ensure that the entire certification operation is in the correct condition, and that customers can use Mazda products reliably. To this end, we are working on the following matters that we consider particularly important.
I reiterate our commitment to our customers that we thoroughly comply with laws and regulations in our certification operations, and that the compliance should take precedence over costs and schedules.
Organization and Responsibility System
As part of a system to check whether tests were conducted in compliance with certification laws and regulations, and to reorganize the governance system, we appointed a chief certification auditor in July 2024, as the person in charge of audits related to certification operations. The chief certification auditor confirms that the testing complies with laws and regulations and that the correctness of the testing by attending the testing.
The management in charge of certification operations at the Company (the person responsible for the overall certification work) is Takeji Kojima, Director and Senior Managing Executive Officer (as of the end of October 2025).
Enhancement Initiatives for Legal Compliance
Mazda is implementing Companywide reforms from the following five perspectives to enhance compliance in its certification processes.
1. Revision of Certification Periods
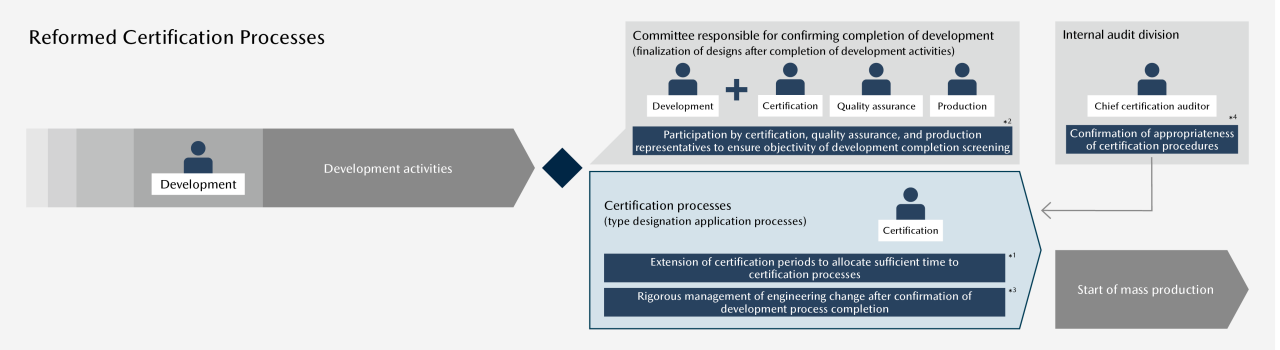
The period for the process from the completion of development to the start of mass production is being extended to accommodate the increased procedures required by tightened regulations. This revision is meant to provide a standardized schedule that prevents excessive physical and mental burdens and allocate sufficient time for ensuring accuracy in certification processes.*1 Furthermore, the committees responsible for approving the completion of development have been elevated to Companywide bodies in order to strengthen management of the steps spanning from development to certification. This change is also meant to heighten objectivity by including representatives from certification, quality assurance, production, and other divisions in addition to development divisions.*2 The resulting frameworks allow for more effective confirmation of preparations for and transition to the certification process.
2. Clarification of Rules for Engineering Change
In principle, any engineering change with the potential to impact product legality or targets must be implemented before the completion of the development process. The committee responsible for confirming the completion of development is expected to confirm whether all changes have been implemented, and there are no more engineering changes after that. Should an engineering change become necessary after the completion of the development process, the heads of development, certification, and quality assurance divisions shall discuss the necessity of the change and whether it should be reflected in prototypes used for certification. These frameworks have been implemented to enhance governance over the certification process.*3
3. Process Digitalization and System Implementation
Automation systems are being introduced to prevent human errors or alterations in the transference, input, and transmission of data and other information during certification processes. We are also examining the possibility of developing frameworks for certification processes in which tablets guide users through test procedures and support them in inputting test results and compiling test reports. Other options being looked at include the development of a comprehensive database for integrating information collected from development divisions and managing records related to application document preparation. The Company aims to introduce such frameworks in April 2026.
4. Enhancement of Staff and Training Programs
The Company is taking steps to ensure and improve the quality of its certification process through phased increases to the staff of certification divisions to accommodate rises in certification workloads and by heightening process efficiency through digital transformation. In addition, all Mazda employees including executives involved in certification processes are required to take part in annual training programs for reviewing fundamental aspects of the legal certification process. The focus of these programs includes prohibition of personal interpretation of certification-related regulations, recent trends in certification systems, actual issues that have occurred at other companies, and the lessons that can be learned from these issues. Through such regular training programs, we seek to ensure that employees have a proper understanding of the relevant regulations as well as high awareness of the importance of compliance with these regulations.
5. Refinement of Testing Infrastructure and Audit Systems
Based on input from individuals involved in actual certification processes, the Company is refining certification testing and other equipment and infrastructure in line with medium-term capital investment plans to ensure that such individuals are adequately equipped to perform appropriate tests. In addition, a chief certification auditor is positioned in internal audit division to verify the appropriateness of test vehicles, equipment, certification testing procedures, and test results. To ensure that the Company’s certification processes are always appropriate, the auditor oversees processes to confirm that issues are being properly identified and addressed as part of the underlying frameworks for processes.*4

Audit, Internal Reporting System, etc.
Mazda has expanded its internal reporting system and internal audits. For example, the Mazda Global Hotline[*] has been established as a system to report the suspicious violations of laws and internal rules, and it has supported to detect and resolve problems related to business processes at an early stage.
In the future, we will further strengthen the system by undergoing internal control evaluations by a third-party organization and by developing a system that is more appropriate for confirming actual vehicles regarding compliance with safety standards after type designation.
[*] The Mazda Global Hotline
An internal reporting system for providing information when it is recognized that a situation is suspicious in violation of laws or internal rules, and that the situation is expected to be unresolved by reporting to the supervisor (through the corporate ladder). This system has been deployed including group companies.